When Jedi Knights have to vanquish an enemy, they whip out their trusty lightsabers. Sooner or later, because of Johns Hopkins researchers, medical doctors searching for to crush most cancers could wield minuscule molecular nanoSABERs that permit them to take a look at tumors in methods by no means earlier than doable.
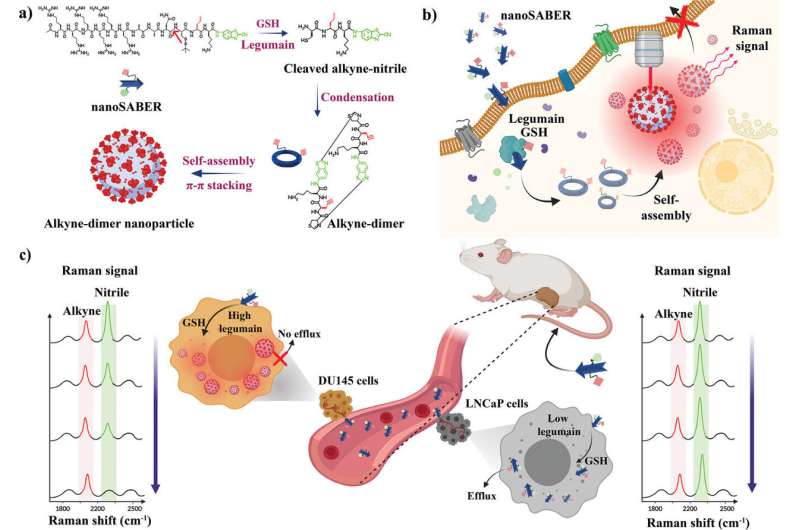
Impressed by the method cells use to assemble proteins, a staff led by two researchers—Ishan Barman on the college’s Whiting Faculty of Engineering and Jeff W. Bulte, a professor of radiology and radiological science on the Faculty of Medication who can also be affiliated with JHU’s Institute for NanoBioTechnology—has created infinitesimal probes that mild up after they encounter sure enzymes present in most cancers cells. The flexibility to visualise tumors of their entirety—and early—may considerably improve most cancers imaging, inform remedy choices, and enhance affected person outcomes.
“This may very well be a recreation changer for most cancers remedy,” mentioned Barman, an affiliate professor of mechanical engineering on the Whiting Faculty, of the self-assembling biorthogonal enzyme recognition (nanoSABER) probes. The staff’s outcomes seem in Superior Science.
At present, tissue biopsies are the gold commonplace for detecting most cancers, although they are often inexact and even miss elements of tumors lurking within the margins. The Johns Hopkins staff’s method may resolve that downside, permitting clinicians to visualise cancerous exercise throughout whole tumors, offering insights into their doable aggressiveness.
Enzymes, particularly legumain, play a number one function within the growth and development of most cancers.
The staff’s new software assembles itself within the presence of those cancer-related enzymes and emits a sign that may then be picked up by Raman spectroscopy, a visualization method that analyzes molecular vibrations to determine and characterize substances. This permits the probes to pinpoint most cancers cells precisely.
The Johns Hopkins staff says its methodology additionally may permit clinicians to extra precisely monitor the buildup of most cancers medicine in tumors throughout remedy, offering a sign of how properly these therapies are working.
“The probes’ means to supply a transparent take a look at the molecular, mobile, and tissue ranges supplies a complete perspective,” mentioned lead writer Swati Tanwar, a post-doctoral fellow in mechanical engineering. “It’s crucial to know what is absolutely taking place on the tumor margins to make sure full most cancers elimination and reduce the possibilities of recurrence.”
Examine co-authors at Johns Hopkins embrace Behnaz Ghaemi, Piyush Raj, Aruna Singh, Lintong Wu, Dian R. Arifin, and Michael T. McMahon. The staff additionally included Yue Yuan of the College of Science and Expertise of China.
Extra data:
Swati Tanwar et al, A Sensible Intracellular Self‐Assembling Bioorthogonal Raman Energetic Nanoprobe for Focused Tumor Imaging, Superior Science (2023). DOI: 10.1002/advs.202304164
Supplied by
Johns Hopkins College
Quotation:
Researchers develop tiny nanoSABERs to assist battle in opposition to most cancers (2023, October 12)
retrieved 14 October 2023
from https://phys.org/information/2023-10-tiny-nanosabers-aid-cancer.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.


