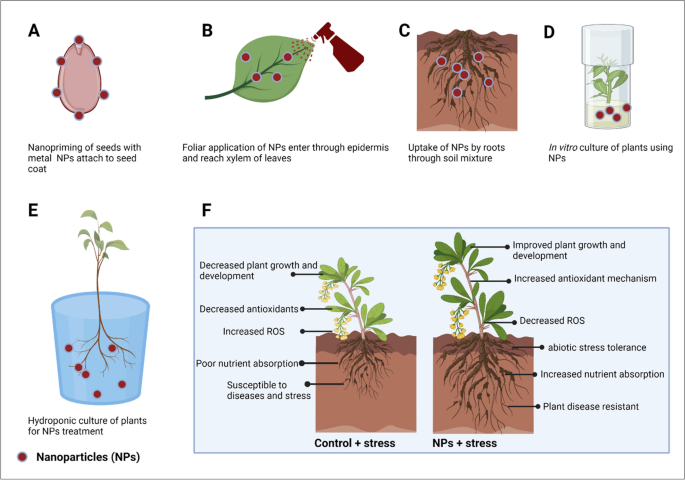
Nanoscience is a trending know-how in plant science that makes use of varied steel NPs as agrochemical carriers or fertilizers have been well known for the previous decade [26]. These NPs present motion in seedling growth, plant progress, germination, root progress [27], elevated carbohydrate metabolism [28], ROS [29] transport of vitamins [30] throughout harassed and non-stressed circumstances. For the appliance of NPs to vegetation, completely different strategies of NPs therapy could be utilized, together with seed priming, foliar spray, and combination with soil, hydroponic tradition for sustainable agriculture (Fig. 4). Nonetheless, one ought to cautiously select therapy choices for NPs utility, as completely different therapy strategies want completely different NPs concentrations, and the usage of increased concentrations of NPs could cause adverse results on vegetation. It’s also apparent that the flawed technique of utility can exhibit toxicity to vegetation, and subsequently, securitizing the tactic relying upon vegetation, nanoparticles, and stress circumstances are essential for sustainable agriculture (Desk 1). Determine 5 exhibiting the attainable phytoxicity response upon nanoparticle utility in vegetation. Subsequently, a number of elements should be thought-about earlier than nanoparticle utility to vegetation (Fig. 3). Amongst varied strategies of utility, seed priming know-how is probably the most popularly used technique to induce the penetration of NPs by means of seeds by way of passive diffusion with water and this technique has proven constructive results. Throughout foliar utility, stomatal permeation, epidermal absorption and internalization are the foremost methods to make foliage to soak up these nanoparticles. This has many benefits that embody serving to to struggle plant ailments and pathogens, offering important micronutrients by means of leaves which might be hardly ever current in nutrition-deficient soil [31,32,33,34]. In contrast to seed priming and foliar utility, a soil combination of NPs, hydroponic tradition or in vitro utility paves the best way for the NPs to straight meet the ecosystem; and should trigger adverse impacts to soil ecosystem. Subsequently, their use should be rigorously thought-about. Owing to benefits and drawbacks of strategies, seed trade is trying to find appropriate priming agent and strategies of utility that might match effectively for sustained agriculture and forestall detrimental results on the ecosystem. Thus, on this part, we focus on about broadly used steel NPs corresponding to AgNPs, AuNPs, ZnONPs and CuNPs with respect to therapy choices and their impact on physiological and biochemical responses of vegetation. As well as, we additionally elaborate the poisonous or unhazardous results of NPs primarily based on the tactic of utility, the focus of NPs, and plant species.
Totally different strategies of NPs utility and their physiological response in vegetation throughout stress and regular circumstances. Based mostly on the cited references, this determine was created utilizing Biorender software program https://biorender.com/
Diagram illustrating phytotoxicity of NPs by means of extreme ROS technology, damaging nuclear materials, cell membranes, and organelles, finally leading to cell loss of life. This determine has been reprinted with permission from [35] Copyright, 2019
AgNPs
AgNPs are a commercialized nanomaterial used within the medical subject as antimicrobial brokers and private care merchandise. As a consequence of their eco-friendly properties, just lately, sufficient curiosity has been developed amongst plant biologists to make use of AgNPs as an environment friendly nanomaterial within the agricultural sector to enhance seed germination, plant progress and growth underneath environmental stress circumstances. Majorly, AgNPs are utilized to vegetation by seed priming know-how, foliar utility or by means of soil combination strategies. Additionally, the advance in plant efficiency had been extremely modulated by the kind of utility used. Subsequently, on this part, we are going to perceive the foremost variations in plant progress and efficiency throughout regular and stress circumstances when completely different strategies of AgNPs therapies are tailored. A biocompatible AgNPs had been synthesized utilizing kaffir lime leaves extract to judge their capability to enhance rice seed germination and starch metabolism after seed priming utility utilizing 5 and 10 mg/L AgNPs underneath regular circumstances [28]. AgNPs penetrated the seed coat and improved the water consumption, elevated ROS and H2O2, and improved seed germination in addition to starch metabolism in comparison with silver nitrate (AgNO3) therapy. These observations aided the speculation of nanopriming of seeds with AgNPs involving the loosening the cell wall of seed coat and endosperms at low concentrations [28]. Furthermore, the minimal nanoparticle focus utilized in seed priming not solely reduces manufacturing prices but additionally mitigates the widespread dispersion of nanoparticles within the atmosphere. Consequently, seed priming emerges as an eco-friendly method.
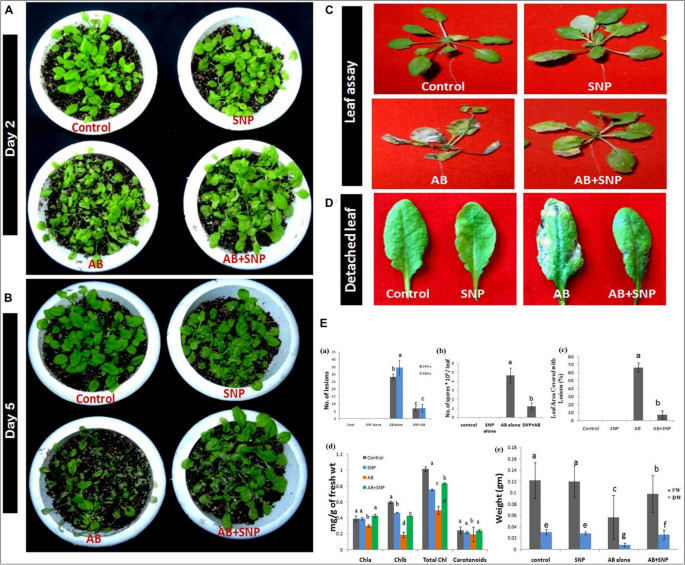
The applying of seed priming additionally minimizes the dispersal of the bigger variety of NPs into ecosystems as NPs therapy utilized to seeds didn’t attain soil and subsequently, could be advised as a promising approach for its industrial use. Nonetheless, one ought to be cautious when utilizing seed priming of AgNPs to enhance seed germination and progress of rice vegetation attributable to their measurement and concentration-dependent responses. Rice seeds soaked with completely different sizes (20, 30–60, 70–120 nm) and concentrations of AgNPs (100 and 1000 mg/L) decreased the germination and progress of rice seedlings. Subsequently, it’s essential to contemplate optimum sizes and concentrations of AgNPs to stop their phytotoxic results in rice seedlings. Throughout seed priming of 60 mg/L AgNPs improved agro-morphological parameters, biochemical parameters, and enzymatic actions in sunflower vegetation. Whereas by means of mixed strategies i.e., seed priming and foliar utility, improved plant yield, seed high quality and secondary metabolite contents of the sunflower vegetation, indicating that every technique of utility could be recruited to enhance distinctive traits of sunflower vegetation. However, 150 mg/L AgNPs by means of soil utility elevated the toxicity in sunflower vegetation by the buildup of AgNPs in root > leaf > stem, which was mirrored from the rise of antioxidants, lipid peroxidation, and lowered contents of chlorophyll, carotenoids, whole carbohydrate, and whole soluble proteins [36]. Comparable phytotoxic results had been reported on the vegetative progress stage in comparison with that of germination in each cucumber and wheat vegetation that had been uncovered to 200 mg/L of AgNPs by means of in vitro utility [37]. In one other examine, constructive impact of urea with low concentrations of AgNPs (10 and 15 mg/L) by means of the appliance of seed priming and foliar utility has been confirmed by way of lowered diseased situation in seeds, increased germination fee, elevated chlorophyll contents, elevated stomatal conductance, and better seedling plenty in oilseed rape and cucumber underneath thermal stress [38]. In eggplant, foliar spray of AgNPs underneath drought circumstances improved progress parameters, photosynthetic pigments, proline, hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and antioxidant actions [39], suggesting the usage of AgNPs can exchange dangerous pesticides and extremely concentrated mineral fertilizers. The pre-treatment of biosynthesized AgNPs with A. brassicicola confirmed vital discount in lesions in comparison with A. brassicicola alone handled vegetation (Fig. 6). These outcomes counsel that the suitable number of AgNPs utility can positively regulate the plant progress and efficiency underneath stress and non-stressed circumstances.
{Photograph} exhibiting impact of silver nanoparticles in decreasing illness severity after (A) 48 h (day 2) submit an infection (B) Day 5 submit an infection (C) discount in necrosis of leaves (D) discount in variety of lesions shaped per leaf (E) Evaluation of illness parameters by way of (a) variety of lesions (b) variety of spores (c) leaf space coated with lesion (d) chlorophyll content material (e) recent and dry weight in silver nanoparticles pre-treated vegetation as in comparison with different therapies. Cont-Management, SNP-Biogenic silver nanoparticles lone, AB-A. brassicicola contaminated vegetation, AB+SNP-A. brassicicola contaminated, handled with SNP, FW-fresh weight, DW-Dry weight. Values are the means ± SD of three replicates. Means sharing completely different alphabets “a”, “b” differ considerably from one another at p ≤ 0.05. This determine has been reprinted with permission from [40] Copyright, 2020
AuNPs
AuNPs had been broadly utilized in varied fields, together with drugs, biology, chemistry, physics, electronics, cosmetics, and so forth. Nonetheless, there’s solely a minimal variety of research reported in vegetation regarding plant progress, growth and phytotoxicity. Typically, the vegetation uncovered to AuNPs exhibited each constructive and adverse results, that are majorly depending on focus, particle measurement, form, and species [41]. The strategy of NP utility to vegetation can also be essential, i.e., whether or not the uptake is thru leaves, roots, or seeds [42]. In vitro examine in Arabidopsis seedlings indicated that direct therapy of the smallest AuNPs of 10 nm on the lowest focus induced root hairs however decreased the quantity and size of lateral roots with increased particle concentrations of AuNPs [43]. In glory lilly, 25 nm sized AuNPs at 500–1000 µM concentrations handled to soil for 40 days elevated the seed germination and vegetative progress [44]. Equally, in maize, 11 nm AuNPs handled at a focus of 5–11 mg/L to soil for 10 days elevated seed germination fee. One other examine on AuNPs synthesized utilizing ecofriendly rhizome extract of galanga plant when utilized by means of seed priming technique, enhanced germination of naturally aged seeds of maize vegetation and improved total progress, with out exhibiting toxicity at 5 to fifteen ppm focus [38]. A foliar spray utility of 10, 25, 50 and 100 mg/L AuNPs had been utilized to Brassica juncea, confirmed that 10 ppm AuNPs elevated a lot of leaves per plant and seed yield. Nonetheless, whole sugar content material elevated when 25 ppm AuNPs had been utilized, indicating that the decrease focus of AuNPs had been ample to boost physiological and biochemical parameters of Brassica sp.[45]. AuNPs are able to inducing stress-related mechanisms to offer resistance to emphasize circumstances in vegetation. For instance, a foliar utility of biosynthesized AuNPs lowered salt stress by sustaining appropriate ratio of reactive oxygen species to reactive nitrogen species (ROS/RNS ratio) and bettering protection mechanism in wheat seedlings. Thus, such AuNPs can be utilized in its place for chemical fertilizers to take care of nutritive standing, stop post-agricultural losses, and mitigate abiotic stresses [46]. In wheat, utilizing seed priming technique, 20 µg/mL AuNPs acted as a signaling molecule underneath chilly stress and activated a protection mechanism by bettering plant progress and photosynthesis [47]. General, AuNPs work finest at decrease concentrations to enhance physiological parameters underneath regular and abiotic stress circumstances (Fig. 7). Along with a physiological response, only a few research on the toxicity of AuNPs in vegetation had been additionally reported. AuNPs therapy affected the expansion and growth of assorted vegetation and confirmed contradictory results relying on the mode of NP utility. When onion vegetation had been handled with 15, 30 and 40 nm sized AuNPs in vitro for 4 h on the focus of 0.1–10 mg/L, authors noticed enhance in chromosomal aberrations and reduce in mitotic index [48]. In barley, 10 nm sized 10 mg/L AuNPs handled in hydroponic medium for two weeks decreased biomass and root size [49]. The administration of spherical gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) by means of hydroponic or soil mixing strategies demonstrated poisonous results. Particularly, within the case of tobacco vegetation, the appliance of twenty-two–25 nm AuNPs in rising concentrations resulted in dose-dependent DNA injury. [50]. Equally, spherical-shaped AuNPs sized 3.5 nm exhibited leaf necrosis impact after 14 days of publicity by transporting in size-dependent mechanisms and translocating to cells and tissues leading to phytotoxicity [51]. To conclude, AuNPs exhibited toxicity in vitro, hydroponic and soil therapy no matter vegetation used and subsequently, seed priming could be tailored for the therapy with AuNPs to enhance plant immunity with out exhibiting poisonous results.
Varied kinds of coatings on the nanoparticles and their affect within the agriculture subject: The steel nanoparticles could be coated with pure natural matter (NOM), amino acids, proteins, antibodies, polymers, surfactants, and negatively or positively charged moieties. Such coatings make the floor of nanoparticles both hydrophilic or hydrophobic and govern their stability in aqueous suspension, dissolution, transport in vegetation, and interactions with plant cells
ZnONPs
Zinc (Zn) is a vital aspect for the plant progress and growth as a result of carbohydrate, protein, and chlorophyll formation considerably lower in vegetation that devoid of Zn. The usage of zinc oxide (ZnO) or ZnSO4.7H2O) as fertilizers are restricted attributable to their low solubility in soil and poor bioavailability of zinc to vegetation. Subsequently, ZnONPs have gotten particular consideration in agriculture subject. Zinc nanoparticles have proven to own the flexibility to penetrate the seed coat that resulted in elevated aquaporin genes concerned in water uptake, seed vigor, bioavailability, solubility in soil, sluggish and gradual launch. The ZnONPs primed seeds had elevated affect on progress and physiology standing in comparison with bulk ZnSO4 therapy, maybe attributable to larger capability to be absorbed and assimilated attributable to nano measurement. In a examine when Zn is added to the primed answer, it improved budding and seedling progress of wheat seedlings, most likely as a result of Zn is concerned within the early levels of coleoptile and radicale growth [52]. The rise of α-amylase in ZnONPs handled seeds can enhance availability of soluble sugars which in flip enhance the germination fee, seedling size, seed water uptake for bettering total metabolic exercise [47]. In comparison with seed priming, foliar spray of ZnONPs used increased quantity of ZnONPs however their use is sort of low in comparison with soil combination technique in wheat vegetation. As an illustration, soil utility of ZnONPs to wheat tissues used whole quantity of 500 mg for 4 plant replicates [53], whereas ZnONPs utilizing foliar spray to wheat tissues used solely 200 mg for 4 replicates denoting the environment friendly use of ZnONPs for bio-fortification in vegetation. This examine additionally confirmed the effectiveness of ZnONPs in bettering the expansion, chlorophyll contents, Zn contents, and by decreasing oxidative stress and cadmium (Cd) contents underneath Cd harassed water-deficient wheat vegetation. We additionally discovered that seed priming of ZnONPs on germination typically is determined by the focus of NPs used, and selection of plant species [54]. As an illustration, underneath 1600 mg/L ZnONPs therapy, germination fee of alfalfa was lowered to 40%, and tomato seeds by 20% however elevated cucumber seed germination in comparison with management, indicating that increased focus of ZnONPs have an effect on the standard of germination. Within the egg plant seeds handled with 100 mg/L ZnONPs, the germination fee was elevated by way of decreasing the seed dormancy [51, 55,56,57] in comparison with foliar spray and soil combination. Equally, there have been concentration-based physiological responses noticed in habanero pepper vegetation when foliar utility was utilized. The foliar spray with completely different concentrations of ZnONPs confirmed completely different functionalities. 1000 mg/L of ZnONPs foliar spray on pepper vegetation triggered constructive impact on plant top, stem diameter, chlorophyll content material, fruit yield and biomass manufacturing; however 2000 mg/L of ZnONPs foliar therapy negatively affected the above parameters. Similar dose resulted in enhance in fruit high quality, capsaicin content material, dihydrocapsaicin, whole phenols and flavonoids in fruits, and enhance antioxidant exercise suggesting that concentration-dependent ZnONPs results in pepper vegetation. Moreover, the seed priming and foliar utility of ZnONPs has additionally proven to exhibit abiotic stress tolerance. The primed wheat seeds used ZnONPs (60 mg/L) to take care of redox homeostasis by decreased ROS technology, and elevated antioxidant enzyme actions corresponding to superoxide dismutase (SOD), peroxidase, thus stopping cells from ROS assault underneath salt stress circumstances. It’s well-known that low degree of Zn is unable to raise ROS attributable to poor activation of antioxidant equipment underneath stress circumstances [58, 59]. One other examine confirmed the appliance of 90 mg/L ZnONPs previous to warmth stress to alfalfa vegetation triggered localization of ZnONPs in vacuoles and chloroplasts, reversed the irregular modifications to chloroplast, mitochondria and cell wall by stimulating antioxidant enzymes and enhancing osmolyte contents, whereas in soil utility that didn’t occur [60]. When cucumber is handled with 100 mg/L ZnONPs by means of foliar utility, the nanoparticles improved drought-associated detrimental results by regulating morphological, physiological, and biochemical attributes. Comparable research of foliar utility of ZnONPs in bettering growth-promoting impact have been reported in wheat, cucumber, and eggplants underneath regular and drought circumstances indicating the function of ZnONPs as a promising fertilizer to enhance progress and stress circumstances.
So far as toxicity is anxious, the foliar utility of ZnONPs confirmed elevated oxidative stress at 400 mg/L. Whereas, the floor modification of 400 mg/L ZnONPs with silicon (Si) improved the steadiness, hydrophilicity of ZnONPs with improved salt tolerance impact with no phytotoxicity. Thus suggesting the usage of ZnO-SiNPs in comparison with ZnONPs in pea vegetation [61]. The adverse impact was additionally noticed when ZnONPs at focus of 500 mg/L was blended in soil. This mixing elevated Zn in roots in comparison with bulk Zn handled pea vegetation resulting in root elongation, translocation of Zn to aerial elements, and elevated H2O2 accumulation in leaves with the discount in antioxidant enzymes corresponding to catalase (CAT), and ascorbate peroxidase (APX). Particularly, after twenty-five days of therapy, there was a major discount in chlorophyll content material, and enhance in lipid peroxidation, indicating the very best toxicity attributable to accumulation in ZnONPs handled pea vegetation that may trigger big adverse affect on ecology and meals chain [62]. Subsequently, it’s needed to pick the NP therapy choices rigorously when contemplating crop well being enchancment utilizing nanomaterials. Equally, in chickpea vegetation devoid of Zn confirmed an elevated in malondialdehyde (MDA) thus leading to decreased biomembrane integrity. Nonetheless, ZnONPs primed seeds reversed Zn content material and decreased MDA by defending membrane integrity [63]. General, ZnONPs utilized by means of seed priming confirmed a constructive impact with out exhibiting toxicity to vegetation in comparison with soil combination and foliar spray. Functionalization of ZnONPs could be really useful to attenuate the poisonous results of ZnONPs when the foliar spray is used. In abstract, selecting the optimum focus of NPs associated to the appliance technique is essential for getting advantages out of NPs.
CuNPs
Copper (Cu) is one other micronutrient for plant progress and growth that’s concerned in lots of biochemical reactions of plant cells. There are additionally a number of research on the appliance of CuNPs to enhance seed yield and high quality underneath regular and stress circumstances. The dose of Cu within the nano or microform (nCu, nCuO, nCu (OH)2-a, nCu (OH)2-b, µCu and µCuO) and CuCl2 are essential for exhibiting useful or detrimental results within the terrestrial ecosystem. As an illustration, cilantro vegetation handled with nCuO from germination to harvesting time has extra adverse results on germination, chlorophyll content material, and plant biomass in comparison with all different Cu primarily based particles indicating the function of nCuO function in exhibiting adverse nutritive results on cilantro vegetation [4]. Equally, research confirmed that seedlings corresponding to Syrian barley[64], soybeans and chickpeas [65], mung beans and wheat [66], radish [6, 67, 68], lettuce [6, 69] had been affected at 0.5 mM nCuO, 500 mg/L, 335 and 570 mg/L, 10 mg/L, 0.1 mg/L inhibited progress fee. Surprisingly, the tactic of CuNPs utility performs very important function in figuring out the nanoparticle toxicity of vegetation. As an illustration, seed priming with 4.44 mg/L CuNPs positively improved plant biomass in regular and drought circumstances. Whereas for bettering the standard of tomato fruits, 250 mg/L CuNPs are really useful because it enhance bioactive elements corresponding to vitamin C, lycopene, whole phenols, and flavonoids by elevated accumulation of antioxidant enzymes corresponding to catalase (CAT) and superoxide dismutase (SOD) [6, 70]. This means that the variations in focus of CuNPs and its affect on vegetation additionally fluctuate relying on the stress circumstances. Vegetation corresponding to lettuce and alfalfa grown in hydroponic tradition with nCu, nCuO, nCu(OH)2-a, nCu(OH)2-b, µCu, and µCuO from 0 to twenty mg/L Cu focus confirmed lowered root size in each the vegetation. Particularly, the translocation of nCu to leaves in lettuce vegetation was noticed solely after therapy with 10 and 20 mg/L concentrations and particularly, in alfalfa vegetation the translocation of nCu was noticed within the dose dependent method. Thus, proving that the alfalfa was extra delicate to nCu in comparison with lettuce vegetation. General, nCu therapies produces differential responses even between the vegetation of dicots. Equally, lettuce grown utilizing hydroponic tradition with 10 and 20 mg/L Cu@CuO and nCuSO4.5H2O confirmed lowered water content material, root size, dry biomass and modified defense-related metabolites in roots [71]. Nonetheless, foliar spray of 1050 mg/L to 2100 mg/L nCu(OH)2-b for the final 4 weeks earlier than harvest didn’t exhibit adverse results as an alternative, it elevated leaf biomass. Nonetheless, there was vital adjustments within the metabolite corresponding to cis-caffeic acid, chlorogenic acid, 3,4-dihydroxycinnamic acid, dehydroascorbic acid occurred, demonstrating the incidence of defensive response towards oxidative stress. Moreover, when cucumber vegetation uncovered to 200–800 mg nCu/Kg in soil elevated Cu accumulation in roots and in a position to translocate considerably to stem, leaves and fruits, inflicting detrimental results. Equally, when Clarika unguiculata (mountain garland) had been uncovered to 10 mg/L nCu(OH)2-b in soil, it utterly arrested photosynthesis and triggered stunted progress in excessive mild ranges and restricted soil circumstances [72]. This indicated that seed priming and foliar spray of CuNPs are comparatively higher than hydroponic tradition and soil therapy for bettering the standard of dicot vegetation (Fig. 8). There are additionally research reported on CuNPs towards biotic stress tolerance.
Constructive and damaging results of various strategies of NPs utility in vegetation relying on this evaluate. This determine was created utilizing biorender software program https://biorender.com/
Micronutrients utilized within the type of nanoparticles confirmed efficacy in rising vegetable and crops yield and reducing fusarium ailments. A foliar utility of 500 μg/mL CuONPs to chrysanthemum plant with or with out Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. chrysanthemi lowered illness severity with a rise in dry biomass, plant top, horticulture high quality [73]. Thus, indicating that CuONPs in a position to enhance total efficiency of chrystanemum vegetation underneath stress or non-stress situation. Moreover, priming of maize seeds with CuNPs exhibited drought tolerance by sustaining leaf water standing, chlorophyll, and carotenoids with decreased ROS and elevated antioxidant enzymes corresponding to SOD, ascorbate peroxidase (APX), and anthocyanin contents [74].