| Sep 01, 2022 |
|
(Nanowerk Information) Composite particles with submicron sizes could be produced by irradiating a suspension of nanoparticles with a laser beam. Violent bodily and chemical processes happen throughout irradiation, a lot of which need to date been poorly understood. Lately accomplished experiments, carried out on the Institute of Nuclear Physics of the Polish Academy of Sciences in Cracow, have shed new mild on a few of these hitherto puzzles.
|
|
When a laser beam strikes agglomerates of nanoparticles suspended in a colloid, occasions happen which are as dramatic as they’re helpful. The large improve in temperature results in the melting collectively of nanoparticles right into a composite particle. A skinny layer of liquid subsequent to the heated materials quickly transforms into vapour, entire sequences of chemical reactions happen below bodily situations that change in fractions of a second.
|
|
Utilizing the strategy introduced right here, known as laser melting, scientists from the Institute of Nuclear Physics of the Polish Academy of Sciences (IFJ PAN) in Cracow not solely produced new nanocomposites, but additionally described among the poorly understood processes liable for their formation.
|
|
“The laser melting course of itself, consisting of irradiating particles of fabric in suspension with unfocused laser mild, has been recognized for years. It’s primarily used for the manufacturing of single element supplies. We, as one among solely two analysis groups on the earth, are attempting to make use of this method to provide composite submicron particles. On this space, the sector remains to be in its infancy, there are nonetheless many unknowns, therefore our pleasure that some puzzles that perplexed us have simply been unravelled,” says Dr. Żaneta Świątkowska-Warkocka, a professor at IFJ PAN, the co-author of a scientific article revealed within the journal Scientific Experiences (“Solvent-particles interactions throughout composite particles formation by pulsed laser melting of α-Fe2O3“).
|
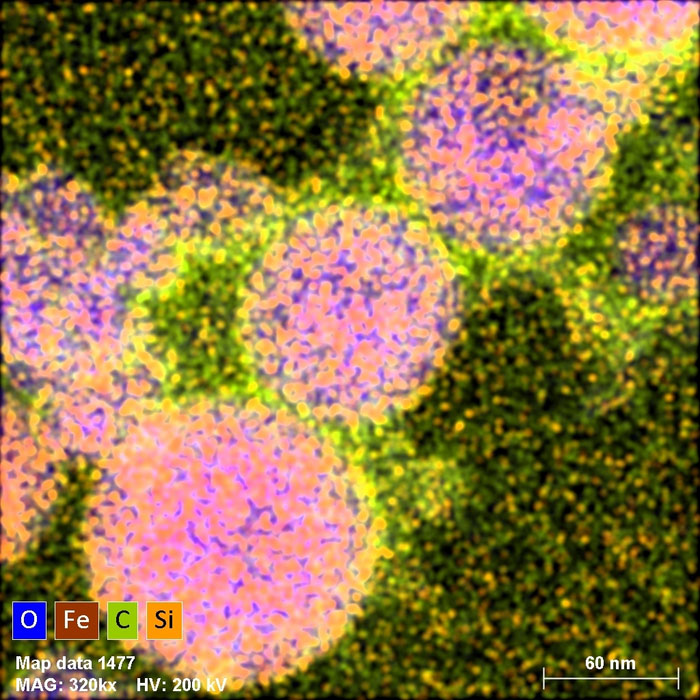 |
| Microscopic picture of nanoparticles of one of many composites obtained by laser melting. False colors depict the distribution of oxygen, iron, carbon and silicon in response to the important thing seen within the decrease left nook. (Picture: IFJ PAN)
|
|
Essentially the most extensively used and on the similar time greatest recognized approach for the synthesis of nanomaterials utilizing laser mild is laser ablation: a macroscopic goal is immersed in a liquid after which pulsed with a targeted laser beam. Beneath the affect of photon impacts, nanoparticles of fabric are torn from the goal and find yourself within the liquid, from which they’ll later be separated fairly simply.
|
|
Within the case of laser melting, the beginning materials is nanoparticles beforehand distributed in the whole quantity of a liquid, the place their unfastened agglomerates are fashioned. The laser beam used for irradiation this time is scattered, however chosen in such a approach as to supply power in quantities enough to soften the nanoparticles. Via laser melting, it’s doable to provide supplies constructed of particles ranging in dimension from nanometers to microns, of assorted chemical buildings (pure metals, their oxides and carbides) and bodily buildings (homogeneous, alloys, composites), together with these troublesome to provide with different methods (e.g. gold-iron, gold-cobalt, gold-nickel alloys).
|
|
The kind of materials fashioned throughout laser melting relies on many parameters. Clearly, the dimensions and chemical composition of the beginning nanoparticles is necessary, as is the depth, effectivity and length of the laser mild pulses. Present theoretical fashions allowed scientists from the IFJ PAN to initially plan the method of manufacturing new nanocomposites, however in apply, the makes an attempt didn’t all the time result in the creation of the supplies that had been anticipated. Clearly, there have been components concerned that had not been taken under consideration within the fashions.
|
|
Dr. Mohammad Sadegh Shakeri, a physicist on the IFJ PAN accountable, amongst others, for the theoretical description of the interplay of nanoparticles with laser mild, presents one of many issues as follows: “The agglomerates of loosely related nanoparticles suspended within the liquid soak up the power of the laser beam, warmth up above the melting level and bond completely, whereas present process larger or lesser chemical transformations. Our theoretical fashions present that the temperature of nanoparticles can improve as much as 4 thousand Kelvin in some instances. Sadly, there aren’t any strategies that may instantly measure the temperature of the particles. But it’s the temperature and its adjustments which are essentially the most important components affecting the bodily and chemical construction of the remodeled materials!”
|
|
With the intention to higher perceive the character of the phenomena occurring throughout laser melting, of their newest analysis physicists from IFJ PAN used alpha-Fe2O3 hematite nanoparticles. They had been launched into three completely different natural solvents: ethyl alcohol, ethyl acetate and toluene. The container with the ready colloid was positioned in an ultrasonic washer, which assured that there can be no uncontrolled compaction of particles. The samples had been then irradiated with laser pulses lasting 10 ns, repeated at a frequency of 10 Hz, which, relying on the model of the experiment, resulted within the formation of particles with sizes starting from 400 to 600 nanometers.
|
|
Detailed analyses of the produced nanocomposites allowed researchers from the IFJ PAN to find how, relying on the parameters of the beam used, it’s doable to find out the important dimension of the particles that first start to alter below the affect of laser mild. It was additionally confirmed that bigger nanocomposite particles attain decrease temperature, with hematite particles of sizes near 200 nm heated to the very best temperature (theoretical estimates instructed right here the worth of 2320 Ok). Nevertheless, essentially the most attention-grabbing leads to the experiments turned out to be these regarding liquids.
|
|
Above all, it was doable to watch a relationship between the dielectric fixed of the liquid and the dimensions of the produced composite particles: the smaller the fixed, the bigger had been the agglomerates. The analyses additionally confirmed the belief {that a} skinny layer of liquid close to a heated nanoparticle undergoes speedy decomposition throughout many chemical reactions. Since these reactions happen in several liquids in a different way, the ensuing supplies additionally differed in construction and chemical composition. The particles produced in ethyl acetate consisted of a virtually uniform magnetite, whereas a magnetite-wustite composite was fashioned in ethyl alcohol.
|
|
“The function of liquids within the manufacturing of nanocomposites by laser melting seems to be extra necessary than everybody beforehand thought. We nonetheless know too little about many issues. Luckily, our present outcomes counsel what the subsequent analysis instructions needs to be. The last word objective is to achieve full information in regards to the processes happening within the colloid and construct theoretical fashions that may enable for the exact design of each nanocomposite properties and strategies of their manufacturing on a bigger scale,” sums up Dr. Świątkowska-Warkocka.
|


