In recent times video conferencing has performed an more and more necessary position in each work and private communication for a lot of customers. Over the previous two years, we’ve enhanced this expertise in Google Meet by introducing privacy-preserving machine studying (ML) powered background options, often known as “digital inexperienced display screen”, which permits customers to blur their backgrounds or exchange them with different photographs. What is exclusive about this answer is that it runs straight within the browser with out the necessity to set up extra software program.
Thus far, these ML-powered options have relied on CPU inference made potential by leveraging neural community sparsity, a standard answer that works throughout units, from entry degree computer systems to high-end workstations. This allows our options to succeed in the widest viewers. Nevertheless, mid-tier and high-end units typically have highly effective GPUs that stay untapped for ML inference, and current performance permits net browsers to entry GPUs through shaders (WebGL).
With the newest replace to Google Meet, we are actually harnessing the facility of GPUs to considerably enhance the constancy and efficiency of those background results. As we element in “Environment friendly Heterogeneous Video Segmentation on the Edge”, these advances are powered by two main parts: 1) a novel real-time video segmentation mannequin and a pair of) a brand new, extremely environment friendly strategy for in-browser ML acceleration utilizing WebGL. We leverage this functionality to develop quick ML inference through fragment shaders. This mixture ends in substantial beneficial properties in accuracy and latency, resulting in crisper foreground boundaries.
 |
| CPU segmentation vs. HD segmentation in Meet. |
Transferring In the direction of Increased High quality Video Segmentation Fashions
To foretell finer particulars, our new segmentation mannequin now operates on excessive definition (HD) enter photographs, somewhat than lower-resolution photographs, successfully doubling the decision over the earlier mannequin. To accommodate this, the mannequin have to be of upper capability to extract options with enough element. Roughly talking, doubling the enter decision quadruples the computation value throughout inference.
Inference of high-resolution fashions utilizing the CPU will not be possible for a lot of units. The CPU could have just a few high-performance cores that allow it to execute arbitrary advanced code effectively, however it’s restricted in its skill for the parallel computation required for HD segmentation. In distinction, GPUs have many, comparatively low-performance cores coupled with a large reminiscence interface, making them uniquely appropriate for high-resolution convolutional fashions. Subsequently, for mid-tier and high-end units, we undertake a considerably sooner pure GPU pipeline, which is built-in utilizing WebGL.
This variation impressed us to revisit a number of the prior design selections for the mannequin structure.
- Spine: We in contrast a number of widely-used backbones for on-device networks and located EfficientNet-Lite to be a greater match for the GPU as a result of it removes the squeeze-and-excitation block, a part that’s inefficient on WebGL (extra under).
- Decoder: We switched to a multi-layer perceptron (MLP) decoder consisting of 1×1 convolutions as a substitute of utilizing easy bilinear upsampling or the dearer squeeze-and-excitation blocks. MLP has been efficiently adopted in different segmentation architectures, like DeepLab and PointRend, and is environment friendly to compute on each CPU and GPU.
- Mannequin dimension: With our new WebGL inference and the GPU-friendly mannequin structure, we have been capable of afford a bigger mannequin with out sacrificing the real-time body price needed for clean video segmentation. We explored the width and the depth parameters utilizing a neural structure search.
 |
| HD segmentation mannequin structure. |
In combination, these adjustments considerably enhance the imply Intersection over Union (IoU) metric by 3%, leading to much less uncertainty and crisper boundaries round hair and fingers.
We have now additionally launched the accompanying mannequin card for this segmentation mannequin, which particulars our equity evaluations. Our evaluation exhibits that the mannequin is constant in its efficiency throughout the assorted areas, skin-tones, and genders, with solely small deviations in IoU metrics.
| Mannequin | Decision | Inference | IoU | Latency (ms) | ||||
| CPU segmenter | 256×144 | Wasm SIMD | 94.0% | 8.7 | ||||
| GPU segmenter | 512×288 | WebGL | 96.9% | 4.3 |
| Comparability of the earlier segmentation mannequin vs. the brand new HD segmentation mannequin on a Macbook Professional (2018). |
Accelerating Net ML with WebGL
One widespread problem for web-based inference is that net applied sciences can incur a efficiency penalty when in comparison with apps operating natively on-device. For GPUs, this penalty is substantial, solely attaining round 25% of native OpenGL efficiency. It is because WebGL, the present GPU normal for Net-based inference, was primarily designed for picture rendering, not arbitrary ML workloads. Particularly, WebGL doesn’t embody compute shaders, which permit for normal goal computation and allow ML workloads in cell and native apps.
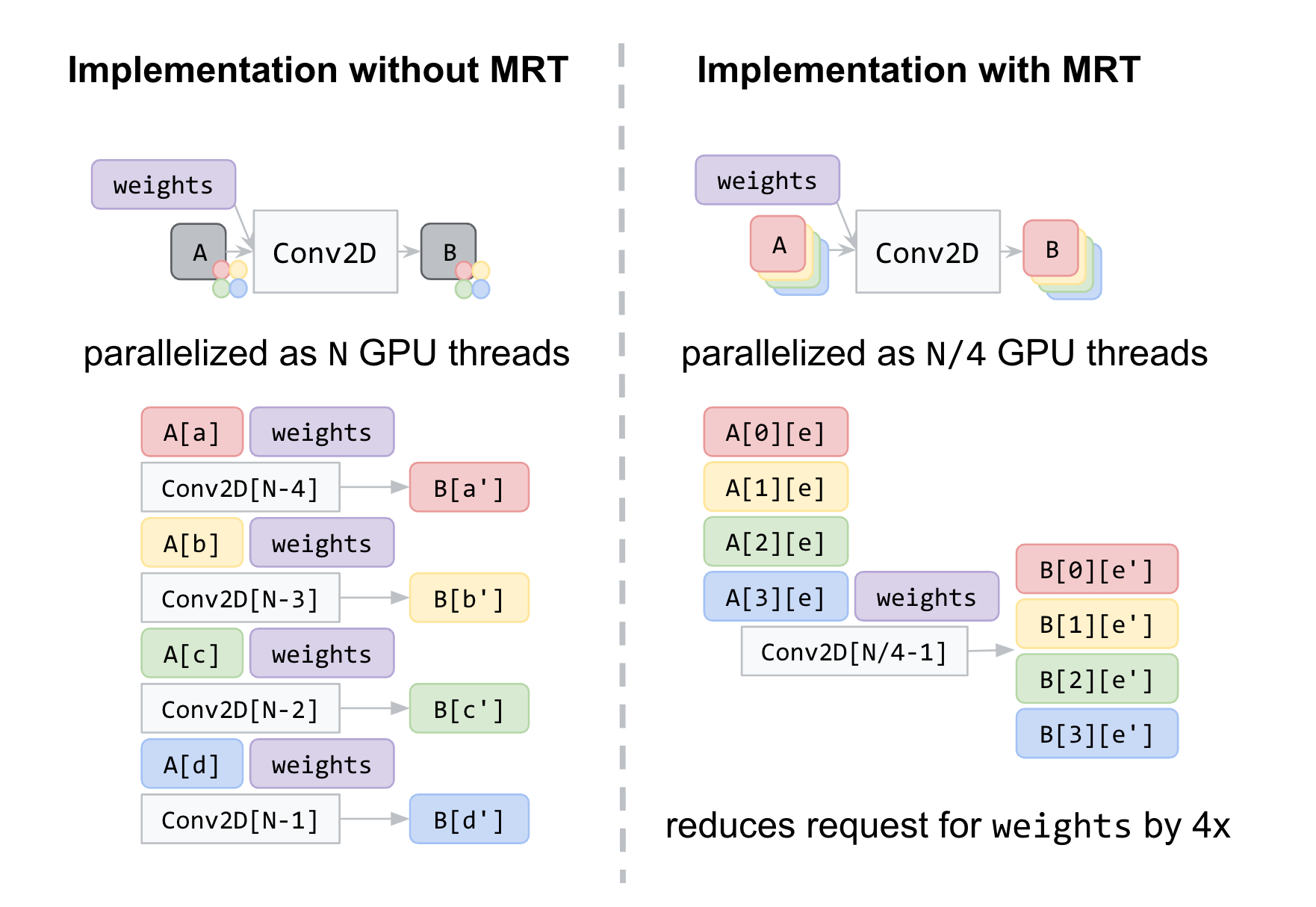
To beat this problem, we accelerated low-level neural community kernels with fragment shaders that usually compute the output properties of a pixel like colour and depth, after which utilized novel optimizations impressed by the graphics neighborhood. As ML workloads on GPUs are sometimes sure by reminiscence bandwidth somewhat than compute, we targeted on rendering strategies that may enhance the reminiscence entry, corresponding to A number of Render Targets (MRT).
MRT is a function in trendy GPUs that permits rendering photographs to a number of output textures (OpenGL objects that signify photographs) without delay. Whereas MRT was initially designed to help superior graphics rendering corresponding to deferred shading, we discovered that we may leverage this function to drastically scale back the reminiscence bandwidth utilization of our fragment shader implementations for crucial operations, like convolutions and absolutely related layers. We accomplish that by treating intermediate tensors as a number of OpenGL textures.
Within the determine under, we present an instance of intermediate tensors having 4 underlying GL textures every. With MRT, the variety of GPU threads, and thus successfully the variety of reminiscence requests for weights, is diminished by an element of 4 and saves reminiscence bandwidth utilization. Though this introduces appreciable complexities within the code, it helps us attain over 90% of native OpenGL efficiency, closing the hole with native purposes.
Conclusion
We have now made fast strides in bettering the standard of real-time segmentation fashions by leveraging the GPU on mid-tier and high-end units to be used with Google Meet. We stay up for the probabilities that will likely be enabled by upcoming applied sciences like WebGPU, which carry compute shaders to the net. Past GPU inference, we’re additionally engaged on bettering the segmentation high quality for decrease powered units with quantized inference through XNNPACK WebAssembly.
Acknowledgements
Particular because of these on the Meet crew and others who labored on this undertaking, specifically Sebastian Jansson, Sami Kalliomäki, Rikard Lundmark, Stephan Reiter, Fabian Bergmark, Ben Wagner, Stefan Holmer, Dan Gunnarsson, Stéphane Hulaud, and to all our crew members who made this potential: Siargey Pisarchyk, Raman Sarokin, Artsiom Ablavatski, Jamie Lin, Tyler Mullen, Gregory Karpiak, Andrei Kulik, Karthik Raveendran, Trent Tolley, and Matthias Grundmann.