A brand new photocatalytic platform for the majority manufacturing of hydrogen has been developed by a analysis group headed by Professor Taeghwan Hyeon on the Middle for Nanoparticle Analysis throughout the Institute for Primary Science (IBS) in Seoul, South Korea.
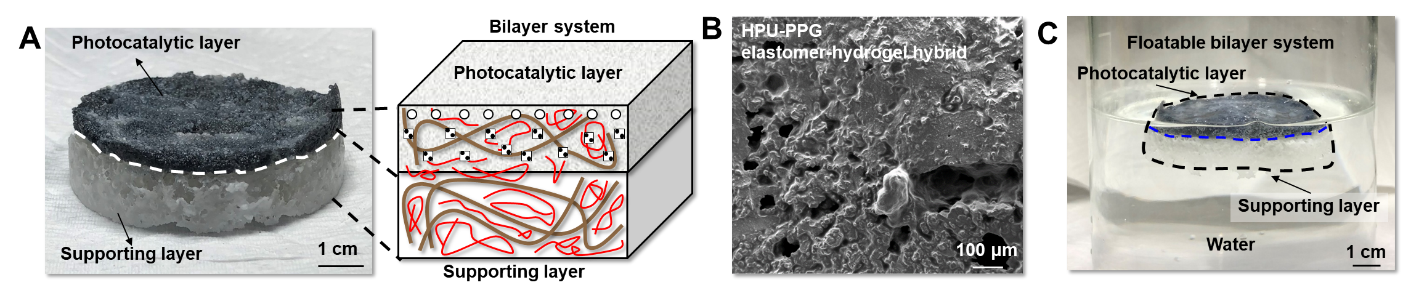
The examine carried out by the group on the photocatalytic platform resulted within the improvement of a floatable photocatalytic matrix. This allows efficient hydrogen evolution reactions with clear advantages over conventional hydrogen manufacturing platforms like movie or panel varieties.
In latest occasions, the importance of different power has risen on account of international challenges, comparable to local weather change and environmental air pollution. Among the many availability of quite a few candidates for different power sources, hydrogen power harvested by photocatalysis is particularly emphasised for its sustainable inexperienced power manufacturing.
Consequently, a lot analysis and improvement have been made to enhance the photocatalysts’ intrinsic response effectivity. A examine carried out on the shape issue of photocatalytic techniques is important for his or her sensible software and commercialization, and it’s but to be explored actively.
Present techniques out there have the potential to repair catalyst powder or nanoparticles onto completely different surfaces, comparable to film-type, particulate sheet-type, and flat panel-type platforms, which have been submerged beneath water.
They skilled sensible issues, comparable to poor mass switch, leaching of catalysts, and reverse reactions. In addition they want further units to isolate and collect the produced hydrogen from water, which provides to the complication of the machine and raises the prices.
On the Middle for Nanoparticle Analysis throughout the IBS, the analysis group, headed by Professor Hyeon, developed a brand new type of photocatalytic platform that floats on the water for hydrogen manufacturing to be performed effectively.
This new platform features a bilayer construction comprising a decrease supporting layer and an higher photocatalytic layer. Each layers are made from a porous structural polymer that grants excessive floor stress to the platform.
The platform has been fabricated as cryo aerogel, a strong substance crammed with gasoline, displaying low density. Consequently, this elastomer-hydrogel fastened with photocatalysts may float on water.
Clear advantages have been exhibited by this platform within the photocatalytic hydrogen evolution response: initially, mild attenuation by water is averted, resulting in efficient photo voltaic power conversion. Secondly, the product, hydrogen gasoline, could possibly be subtle rapidly into the air, avoiding reverse oxidation reactions and conserving excessive response yield.
Thirdly, because of its porosity, the water could possibly be equipped simply to the catalysts located contained in the elastomer-hydrogel matrix. Lastly, catalysts have been immobilized throughout the matrix for long-term operation with out leaching points.
In comparison with the standard submerged platform, the scientists experimentally proved the wonderful hydrogen evolution efficiency of the floatable platform. Furthermore, the platform’s scalability, which is critical for potential industrialization, was additionally illustrated beneath pure daylight.
It was verified that round 80 mL of hydrogen could possibly be generated by the floatable photocatalytic platform with the assistance of titania catalysts and a single copper atom with an space of 1 m2. Even after two weeks of operation in seawater consisting of a number of microorganisms and floating matter, the platform’s hydrogen evolution efficiency was not compromised.
The proposed platform may even produce hydrogen from options that dissolve family waste, comparable to polyethylene terephthalate bottles. Consequently, the platform is usually a answer for recycling wastes, which contributes to an environment-friendly society.
Jeong Hyun Kim, Middle for Nanoparticle Analysis, Institute for Primary Science
Notably, this examine grants a generalized platform for efficient photocatalysis that’s not simply restricted to hydrogen manufacturing. It’s potential to substitute the catalytic element for a number of most popular makes use of with out altering the floatable aerogel materials properties of your entire platform.
This ensures the in depth applicability of the platform to different photocatalytic reactions, comparable to oxygen hydrogen peroxide manufacturing, evolution response, and era of a number of natural compounds.
This examine makes nice progress within the area of photocatalysis and showcases the potential of inexperienced hydrogen manufacturing at sea with world-class efficiency. The distinctive materials options, excessive efficiency, and broad applicability within the area of photocatalysis of our platform will undoubtedly open a brand new chapter in different power.
Taeghwan Hyeon, Professor, Middle for Nanoparticle Analysis, Institute for Primary Science
Journal Reference
Lee, W. H., et al. (2023) Floatable photocatalytic hydrogel nanocomposites for large-scale photo voltaic hydrogen manufacturing. Nature Nanotechnology. doi.org/10.1038/s41565-023-01385-4.
Supply: https://www.ibs.re.kr/eng.do


