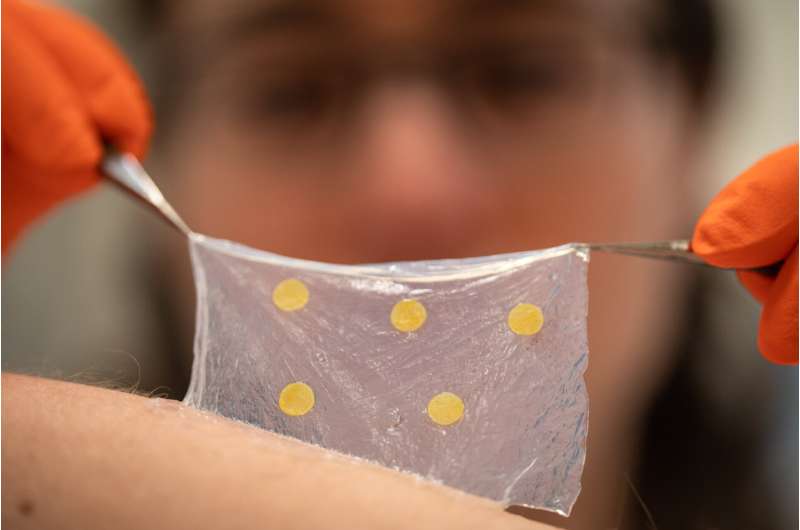
A nanocellulose wound dressing that may reveal early indicators of an infection with out interfering with the therapeutic course of has been developed by researchers at Linköping College, Sweden. Their examine, printed in Supplies Immediately Bio, is one additional step on the street to a brand new sort of wound care.
The pores and skin is the biggest organ of the human physique. A wound disrupts the traditional perform of the pores and skin and may take a very long time to heal, be very painful for the affected person, and will—in a worst-case state of affairs—result in dying if not handled appropriately. Additionally, hard-to-heal wounds pose a terrific burden on society, representing about half of all prices of out-patient care.
In conventional wound care, dressings are modified repeatedly, about each two days. To verify whether or not the wound is contaminated, care employees must raise the dressing and make an evaluation based mostly on look and checks. It is a painful process that disturbs wound therapeutic because the scab breaks repeatedly. The chance of an infection additionally will increase each time the wound is uncovered.
Researchers at Linköping College, in collaboration with colleagues from Örebro and Luleå Universities, have now developed a wound dressing product of nanocellulose that may reveal early indicators of an infection with out interfering with the therapeutic course of.
“Having the ability to see immediately whether or not a wound has develop into contaminated, with out having to raise the dressing, opens up for a brand new sort of wound care that may result in extra environment friendly care and enhance life for sufferers with hard-to-heal wounds. It will probably additionally scale back pointless use of antibiotics,” says Daniel Aili, professor within the Division of Biophysics and Bioengineering at Linköping College.

The dressing is product of tight mesh nanocellulose, stopping micro organism and different microbes from getting in. On the similar time, the fabric lets gases and liquid by, one thing that’s necessary to wound therapeutic. The concept is that when utilized, the dressing will keep on throughout your complete therapeutic course of. Ought to the wound develop into contaminated, the dressing will present a coloration shift.
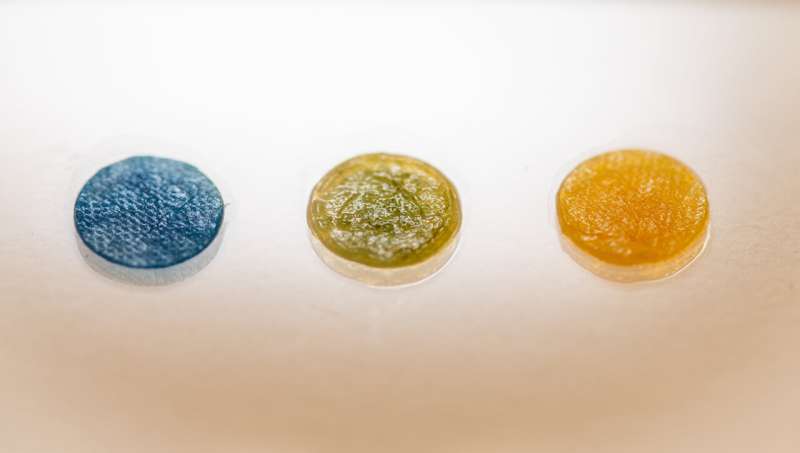
Non-infected wounds have a pH worth of about 5.5. When an an infection happens, the wound turns into more and more fundamental and will have a pH worth of 8, and even larger. It’s because micro organism within the wound change their environment to suit their optimum progress surroundings. An elevated pH worth within the wound might be detected lengthy earlier than any pus, soreness or redness, that are the most typical indicators of an infection.
To make the wound dressing present the elevated pH worth, the researchers used bromthymol blue, BTB, a dye that adjustments coloration from yellow to blue when the pH worth exceeds 7. For BTB for use within the dressing with out being compromised, it was loaded onto a silica materials with pores just a few nanometers in dimension. The silica materials may then be mixed with the dressing materials with out compromising the nanocellulose. The result’s a wound dressing that turns blue when there may be an an infection.
Wound infections are sometimes handled with antibiotics that unfold all through the physique. But when the an infection is detected at an early stage, native remedy of the wound might suffice. This is the reason Aili and his colleagues at Örebro College are additionally creating anti-microbial substances based mostly on so-called lipopeptides that kill off all forms of micro organism.
“The usage of antibiotics makes infections more and more problematic, as multi-resistant micro organism have gotten extra widespread. If we will mix the anti-microbial substance with the dressing, we reduce the chance of an infection and scale back the overuse of antibiotics,” says Aili.
Aili says that the brand new wound dressing and the anti-microbial substance are a part of creating a brand new sort of wound remedy in out-patient care. However as all merchandise for use in medical care settings must move rigorous and costly testing, he thinks that will probably be 5 to 10 years earlier than will probably be accessible there.
Extra data:
Olof Eskilson et al, Nanocellulose composite wound dressings for real-time pH wound monitoring, Supplies Immediately Bio (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2023.100574
Supplied by
Linköping College
Quotation:
Researchers develop wound dressing that may reveal an infection (2023, April 18)
retrieved 18 April 2023
from https://phys.org/information/2023-04-wound-reveal-infection.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.


