Technical debt is a widely known software program engineering concern that refers back to the tradeoff between the short-term advantages of fast supply and the long-term worth of growing a software program system that’s simple to evolve, modify, restore, and maintain. Technical debt in a code base contains these structural parts that, if not reworked, contribute to accumulation of elevated operation and upkeep prices. On this weblog put up, we look at the evolution of the sector of technical debt and determine open analysis questions that can drive future developments.
Researchers and organizations in authorities and trade acknowledge that if you don’t actively handle technical debt, it can handle you. The U.S. Division of Protection has affirmed the significance of technical debt by particularly citing it within the Nationwide Protection Authorization Act of 2022. Part 836 of this act authorizes the U.S. secretary of protection to provoke a examine of technical debt in software-intensive methods that features analyses and actionable, particular steering and proposals for statutory or regulatory modifications.
Our work in technical debt is based on the precept that for those who don’t make one thing seen, you gained’t handle it. Avoiding the destructive outcomes related to accumulating technical debt requires organizations to embrace technical debt administration as a core software program engineering apply. Simply utilizing the phrase “technical debt” will not be an engineering apply. We have now lengthy really useful that technical debt be added to an points backlog to research how and the place structure necessities is likely to be failing and that it’s managed as an integral a part of product-development actions.
In Search of a Metric for Technical Debt
Though there are a number of metrics in use right this moment that purpose to quantify technical debt from totally different views—and there’s no one-size-fits-all metric—we’re gratified by the affect that our work on technical debt metrics has had on the sector of software program engineering. The Worldwide Convention on Software program Structure (ICSA) just lately awarded us with the Most Influential Paper Award for a paper we wrote in 2012, In Search of a Metric for Architectural Technical Debt, together with our colleagues Philippe Kruchten and Marco Gonzalez-Rojas of {the electrical} and pc engineering division on the College of British Columbia. Within the paper, we detailed how technical debt is rooted in software program structure and described how an architecture-focused and measurement-based strategy to growing a metric based mostly on propagation value helps strategically handle technical debt. We demonstrated this strategy by making use of it to a system-development effort that was then underway.
The technical debt idea has confirmed to be a helpful assemble for speaking the tradeoff between fast supply and long-term system sustainability. Its affect is clear in Agile at scale and DevSecOps practices, in addition to in authorities acquisition practices, such because the Adaptive Acquisition Framework and the Sensible Software program and Methods Measurement Steady Iterative Growth (Agile) Measurement Framework.
Sadly, our use of the time period architectural technical debt within the title of our paper has been taken by some to suggest that there’s a taxonomy of varied sorts of technical debt, of which architectural technical debt is only one. We subsequently hear and skim of documentation technical debt, safety technical debt, and so forth. You will need to make clear that this interpretation was not our intention. Our view is that technical debt is rooted in architecture- and design-related points and the rework that these points trigger. When not managed, technical debt will increase the probability of safety points and defects that additional improve the accumulating penalties.
Technical Debt is Rooted in Structure Rework
The essence of our strategy—each after we wrote the paper and now—is that this: The worth of the delivered options and the affect of value that might be incurred should be taken into consideration in decision-making associated to delivering a product. Making technical debt seen supplies the required info for making knowledgeable selections about managing the potential affect of rework over time. Within the curiosity of creating debt seen, our paper introduced a dependency-analysis framework for measuring structure rework as a proxy for technical debt.
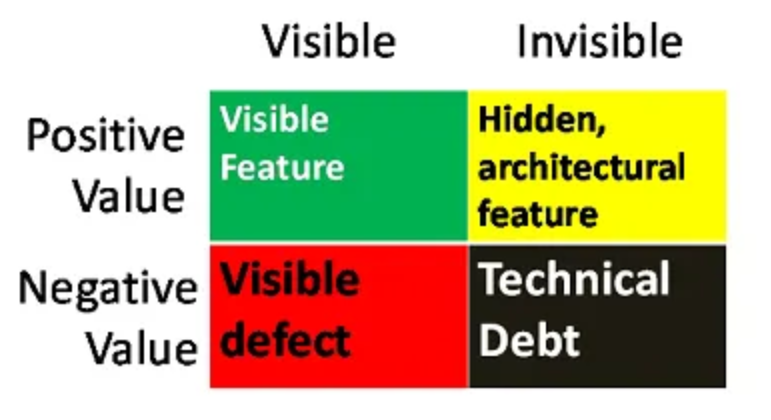
Our colleague and co-author Philippe Kruchten posed a helpful method of characterizing parts in a software-development challenge all through the event lifecycle. These parts are depicted in Determine 1.
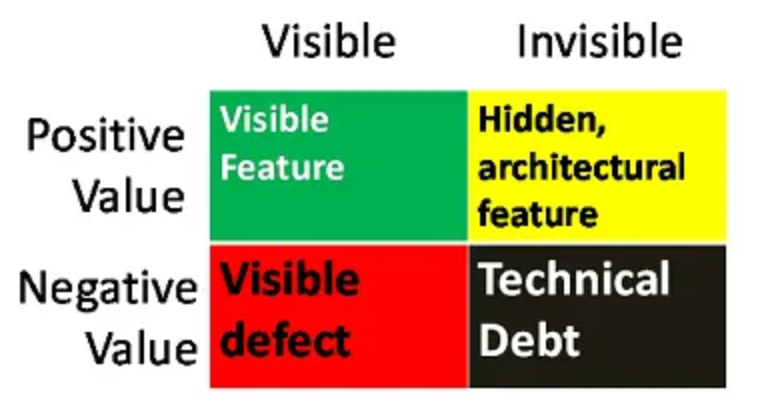
Optimistic-value elements are proven on the highest row of Determine 1. The inexperienced represents the options and performance that the challenge should ship for its stakeholders, which is seen on the discharge schedule and drives the group, the gross sales, the success, and the shopper satisfaction. The yellow represents the architectural infrastructure and design constructs which are important for the longevity, construction, and habits of the system and for reaching its supposed high quality attributes. Options are seen to the consumer and the structure is invisible to the world outdoors of the event workforce, although each add optimistic worth.
Equally, now we have the negative-value elements proven within the backside row of Determine 1. The purple represents defects which are seen to the consumer and should be managed as shortly as doable to keep away from jeopardizing the system. The black represents technical debt that is a component invisible to the skin world ensuing from not getting the complete structure necessities proper. Technical debt accumulates because the product is constructed and key selections are deferred or poor work is finished.
The dependency framework we described in that paper takes into consideration how structure allows performance and the way builders can ship performance whereas additionally attending to the structure within the quick time period and the long run. Within the paper, we in contrast two paths, proven in Determine 2.
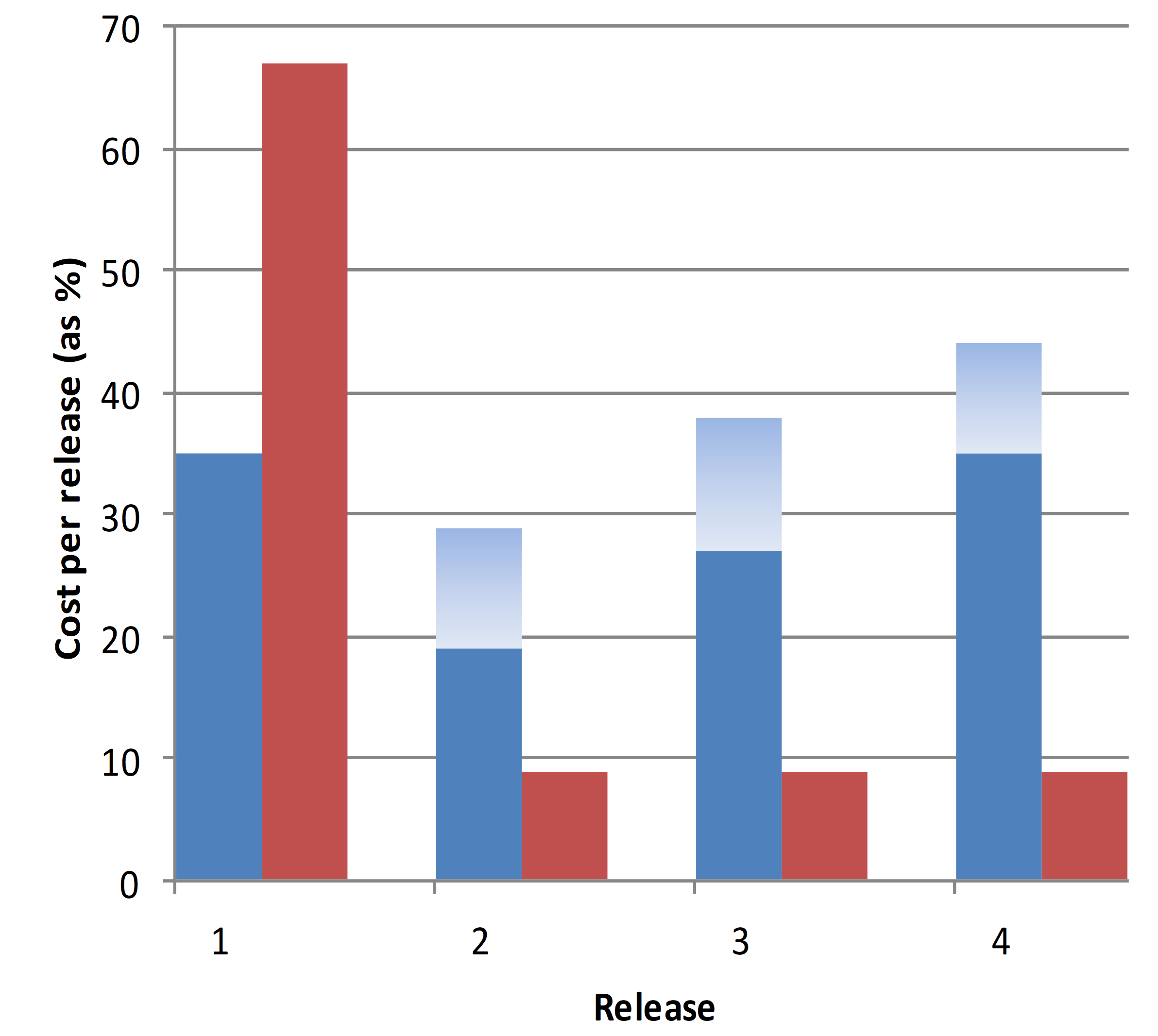
Determine 2: Comparability of Growth Paths
We discuss with Path 1, proven in blue in Determine 2, because the ship quickly path. It begins by delivering worth however more and more incurs rework (proven within the lighter shade of blue). We name Path 2, proven in purple, the architecture-savvy or cut back rework and allow compatibility path. This path initially incurs a better value, however the price of the rework is extra constant as the required structure is in place to assist subsequent iterations.
The purpose of making a path comparability is to make the tradeoffs seen and specific. Path 1 represents the case of when the system is new and its enterprise worth is being explored and found. In such circumstances, it’s paramount to ship some performance and to check it within the subject. As using the system proves helpful, the system begins to develop. Within the instance we describe within the paper, following the preliminary technique created uncontrolled implementation prices, requiring a major re-architecting effort, which was suboptimal for the long-term sustainment of the system. Performing such evaluation on potential rework because the system grows can allow well timed selections about when to begin re-architecting the system or when to pay again the curiosity on the borrowed time of the sooner design selections. Our strategy supplied concerns on the structure stage for making rework specific at every launch.
Our paper additionally demonstrated how software program architects can make the most of a change-propagation metric to calculate and justify the price of taking up technical debt. The quantification of rework will not be trivial, nevertheless, particularly in terms of structure. Whereas nobody metric alone can assist builders optimize improvement value over time, structural structure evaluation and associated practices present the attitude wanted to make the price of implementing the chosen choices specific.
Observe-Up Analysis
Our paper influenced quite a few analysis strategies and software program instruments within the 10 years since its publication, a lot of which have been validated in industrial case research with software-development firms. One of these follow-up work takes into consideration how structure allows performance and methods to obtain the steadiness between delivering performance and listening to structure in each the quick and long run. Examples of this work embody the next:
Future Work in Technical Debt
As time has handed, the physique of labor on understanding and managing technical debt and structure evolution has grown. On the SEI, we plan to research how empirical information and evaluation can be utilized to enhance iterative and incremental structure practices to handle technical debt.
A big quantity of analysis stays to create a technical debt quantification framework that isn’t solely repeatable and dependable, but additionally cognizant of domain-specific system challenges. We encourage researchers in each software program structure and metrics to extra deeply discover the connection between the construction and habits of structure patterns and the way metrics behave.
Sooner or later, it is going to be vital to obviously set up the validity of rising methodologies for quantifying technical debt. Not all present metrics for characterizing and quantifying technical debt are confirmed and never all are trivial to make use of. Whereas instruments are rising in sophistication, they have an inclination to concentrate on the issue of structure conformance somewhat than on the architectural elements of quantifying rework.
Key open analysis questions within the subject of technical debt analysis embody the next:
- How will we quantify rework utilizing totally different metrics to information how and when to refactor methods to resolve technical debt?
- How will we refactor methods, particularly accurately incorporating related metrics and power assist?
- How can we relate rework quantification to operational practices?
- How will we seize the empirical information that’s coming from trade and authorities, analyze them, and use them to tell the correct use of iterative, incremental structure practices and methods to enhance these practices together with managing technical debt.
We’d welcome the chance to work immediately with organizations fascinated by collaborating with us on this work. Please contact us at information@sei.cmu.edu.
We additionally encourage researchers to contemplate engaged on looking for solutions to the questions above and to change into concerned within the annual TechDebt Convention. This convention connects main software program engineering researchers and practitioners to debate approaches for managing varied sorts of technical debt, to share experiences and concepts, and to determine key challenges for trade and academia. It supplies a chance to vet concepts amongst distributors, trade builders, and researchers in technical debt administration.