A perfect nanovesicle to struggle most cancers would have three functionalities: 1) a precision-targeting molecule to preferentially bind it to floor markers on most cancers cells, 2) a strongly certain radionuclide sign that might enable a PET scan to find the vesicles within the physique, and three) the flexibility to hold and launch a drug remedy, resembling a chemotherapy, on the most cancers tumor.
It could additionally meet two different necessities—having a easy and facile technique of manufacture, and being biocompatible and biodegradable within the physique.
A College of Alabama at Birmingham workforce has now described a tiny polymersome that—in preliminary preclinical experiments—seems to satisfy these hurdles. Every polymersome is a hole sphere with a skinny wall, however it’s the coating on the polymersome that marks a step ahead.
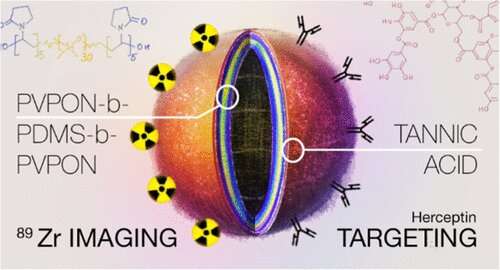
The 60-nanometer triblock copolymer polymersomes have degradable tannic acid, or TA, adsorbed onto the floor by means of hydrogen bonding. That TA, in flip, is ready to rapidly and stably bind a monoclonal antibody-targeting molecule and zirconium radionuclide, or Zr, with out the necessity to construct particular linkers, resembling chelators, say Eugenia Kharlampieva, Ph.D., and Suzanne E. Lapi, Ph.D., leaders of the UAB workforce. Their research is revealed within the journal Biomacromolecules.
“On this research, we’ve got developed a easy strategy for a chelator-free modification of the PVPON5-PDMS30-PVPON5 triblock copolymer nanovesicles, about 60 to 80 nanometers in diameter, with a layer of polyphenol that may be concurrently used to anchor 89Zr radiotracer or different energetic steel ions for molecular imaging, and a HER2-targeting ligand, trastuzumab monoclonal antibody, for nanovesicle concentrating on to HER2-positive breast most cancers cells,” mentioned Kharlampieva, a distinguished professor within the UAB School of Arts and Sciences’ Division of Chemistry. PVPON5 is a brief, five-monomer hydrophilic polymer block, and PDMS30 is an extended, 30-monomer, hydrophobic polymer block throughout the triblock copolymer.
Breast most cancers is among the commonest most cancers ailments, and international charges of loss of life are nonetheless excessive. Systemic medication or therapeutic antibodies are present therapies, however they’re usually related to coronary heart injury and dysfunction. Picture-guided drug supply to a strong tumor may enable efficient drug exercise with diminished drug toxicity.
“To the most effective of our information, our work represents the primary instance of a chelator-free-radiolabeled polymersome able to a long-term multiday PET imaging research in vivo,” mentioned Lapi, director of the UAB Cyclotron Facility and a professor within the UAB Division of Radiology. “The radiolabeling strategy developed herein can probably present steady binding of a large spectrum of isotopes with out radiometal leaching from the vesicle membrane in vivo. Notably, this strategy integrates the inherent benefits of a polyphenolic polymersome membrane with the advantage of rapidly anchoring breast most cancers cell-targeting ligands.”
Within the research, TA on the polymersome certain 89Zr4+ radionuclide by means of nonspecific ionic pairing, and the TA additionally certain the trastuzumab monoclonal antibody, or Tmab, by means of hydrogen bonding and ionic pairing. There was wonderful retention of the 89Zr for as much as seven days, as confirmed by PET scans in wholesome mice.
“The noncovalent Tmab anchoring to the polymersome membrane will be extremely advantageous for nanoparticle modification in comparison with at the moment developed covalent strategies, because it permits simple and fast integration of a broad vary of concentrating on proteins,” Kharlampieva mentioned. “Given the flexibility of those polymersomes to encapsulate and launch anticancer therapeutics, they are often additional expanded as precision-targeted therapeutic carriers for advancing human well being by means of extremely efficient drug-delivery methods.”
One hour of incubating the TA-polymersomes in an answer of 89Zr-oxalate led to radiolabeling yields of 97 p.c, and people yields remained constant over one, three and 7 days. The labeled polymersomes weren’t cytotoxic when incubated in vitro with two traces of most cancers cells as much as 4 days. Moreover, binding of 89Zr to polymersomes with Tmab already hooked up additionally had excessive yields of 97 p.c and stability by means of seven days. These binding yields are sufficiently excessive for medical use, the UAB researchers say.
Subsequent, the steady retention of the 89Zr on the TA-polymersomes was demonstrated not directly in mice.
The biodistribution of free 89Zr radiotracer has been beforehand reported to localize largely within the backbone and femurs of animals as a result of chelation of the zirconium with phosphate moieties within the bone. The UAB researchers discovered that, when free 89Zr was injected into mice, almost all of it was positioned within the femur bones after 24 hours, as measured by a PET scan. A significantly totally different biodistribution was seen when 89Zr-TA-polymersomes had been injected into mice. Negligible radioactivity was present in bones; as an alternative, almost all of the radioactivity was within the spleen and liver. That location represents the identified anticipated clearance of nanovesicles by means of the mononuclear phagocyte system for nanomaterials bigger than 6 to eight nanometers.
“The noticed drastic distinction between the biodistribution of the free 89Zr and the steel radiotracer-labeled vesicle is essential, because it demonstrates an unimpeded functionality of the polymeric nanocarrier to be tracked in vivo,” Lapi mentioned.
The robust imaging distinction within the mice was retained by means of seven days, additional proof of tight retention of the 89Zr on the TA-polymersomes.
The flexibility of the 89Zr-Tmab-TA-polymersomes to focus on HER2-positive most cancers cells was proven in vitro by differential binding of the nanovesicles to HER2-positive breast most cancers cells versus HER2-negative cells. The researchers say additional testing to focus on breast most cancers tumors in animals is warranted.
Co-first authors of the research, “Direct radiolabeling of trastuzumab-targeting triblock copolymer vesicles with 89Zr for positron emission tomography imaging,” are Veronika Kozlovskaya, UAB Division of Chemistry, and Maxwell Ducharme, UAB Division of Radiology.
Different co-authors with Kharlampieva, Lapi, Kozlovskaya and Durcharme are Maksim Dolmat and James M. Omweri, UAB Division of Chemistry; and Volkan Tekin, UAB Division of Radiology.
Extra data:
Veronika Kozlovskaya et al, Direct Radiolabeling of Trastuzumab-Concentrating on Triblock Copolymer Vesicles with 89Zr for Positron Emission Tomography Imaging, Biomacromolecules (2023). DOI: 10.1021/acs.biomac.2c01539
Supplied by
College of Alabama at Birmingham
Quotation:
Simple and fast binding of concentrating on molecule and radiotracer to drug nanocarrier for most cancers remedy (2023, April 10)
retrieved 10 April 2023
from https://phys.org/information/2023-04-easy-quick-molecule-radiotracer-drug.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.


