Nanodiamond fragments which have been optically trapped are getting used as intracellular sensors by researchers to create a brand new methodology for analyzing the advanced processes inside dwelling cells. The research crew captured the particles contained in the cell at low energy whereas the cell was nonetheless alive utilizing custom-designed optical tweezers.
The analysis marks a major step ahead in quantum sensing, which makes use of quantum mechanics to look at atomic-level modifications.
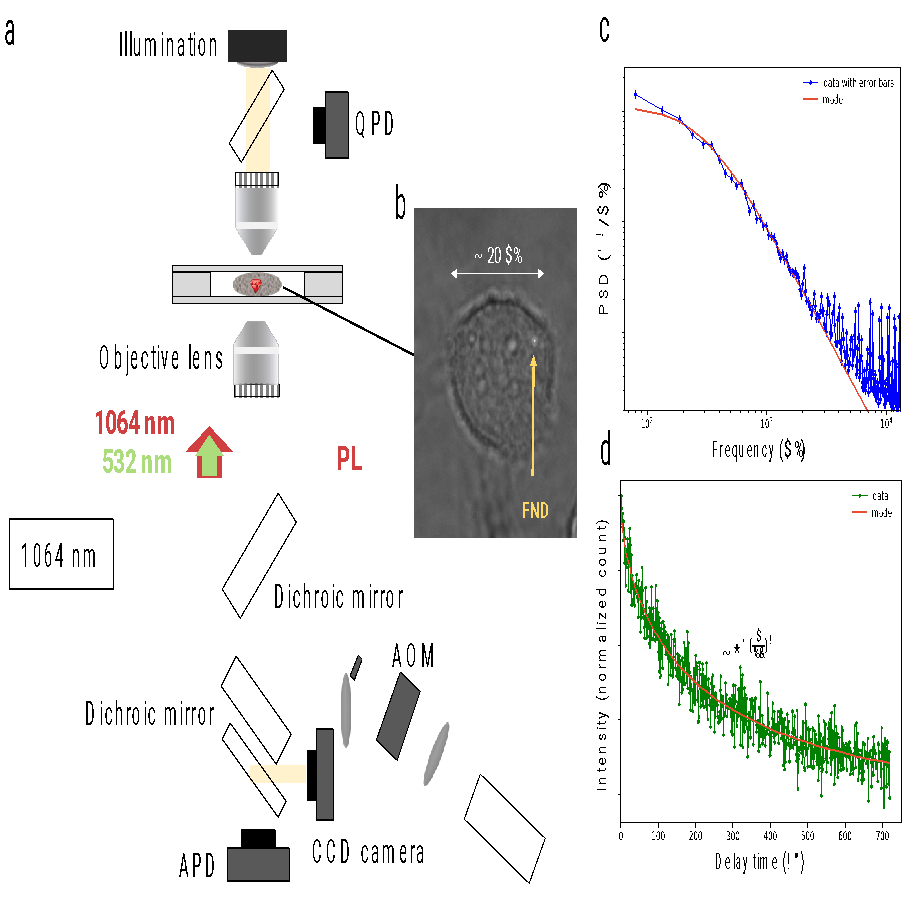
The scientists confirmed how the nanodiamond particles can be utilized to detect magnetic noise contained in the cell after utilizing optical tweezers to seize the particles inside single leukemia cells.
The research will likely be introduced by Fatemeh Kalantarifard from the Technical College of Denmark on the Optica Biophotonics Congress, which is able to happen on-line from April 23–27, 2023, and in Vancouver, British Columbia. The presentation by Kalantarifard is slated to be on Monday, April 24th, 2023, from 15:00 to fifteen:15 PDT. (UTC–07:00).
Optically Trapped Nanodiamonds
Curiosity in fluorescent nanodiamonds (FNDs) has grown as potential emitters and sensors for quite a lot of makes use of. The power of FNDs to sense bodily elements utilizing quantum sensings, equivalent to temperature and magnetic area, is considered one of their most outstanding traits.
The nitrogen-vacancy (NV) heart, a paramagnetic flaw in a diamond that permits studying out temperature and magnetic field-dependent electron spin on the nanoscale, is the muse of diamond quantum sensing.
Just lately, scientists have developed fluorescent nanodiamonds with NV facilities to be used as intracellular sensors. Within the research that was introduced on the convention, scientists merged the trapping of FNDs with spin-based photoluminescence detection strategies typical of diamond-based sensing in a single cell.
Cells from a human leukemia cell line had been used to endocytose FNDs, which had been then captured by the dwelling cell whereas it was uncovered to a low-power near-IR laser (1064 nm wavelength).
Nanoscale Sensing
The researchers carried out T1 relaxometry measurements after the nanodiamonds had been positioned contained in the cells or on the cell floor to judge their sensing skills. By periodically turning on and off a Inexperienced (532 nm wavelength) laser pulse, this system polarizes the NV facilities’ electron spins earlier than permitting them to return to equilibrium.
The spin rest charge is calculated by optically observing the fluorescence depth stage because the polarized configuration displays stronger fluorescence than the equilibrium state.
Researchers can hint the magnetic noise contained in the cell by analyzing the spin rest charges of nanodiamonds positioned in varied areas as a result of the magnetic noise within the setting influences these charges.
The demonstration signifies that optically trapped fluorescent nanodiamonds may function a exact and customizable methodology to measure issues like temperature and magnetic area inside dwelling cells.
The mix of optical trapping of diamond nanoparticles and nanodiamond-based quantum sensing can present a strong instrument for learning cell mechanical properties. Optical trapping may help maintain the nanodiamond-based sensors with excessive precision, permitting for extra correct measurements on the nanoscale stage.
Fatemeh Kalantarifard, Postdoctoral Researcher, Technical College of Denmark
Kalantarifard additional added, “Specifically, T1 relaxometry measurements of optically trapped nanodiamonds can be utilized without cost radical detection in cells. Free radicals are extremely reactive molecules that may trigger harm to cells and tissues. They’re produced naturally within the physique due to metabolism and may also be generated by publicity to environmental elements equivalent to radiation or toxins.”
“The usage of optically trapped nanodiamonds without cost radical detection provides a number of benefits, together with excessive sensitivity, non-invasiveness, and the flexibility to observe real-time modifications in T1 rest time. This method can be utilized to check the results of oxidative stress on cells and should have potential purposes within the prognosis and therapy of ailments equivalent to most cancers and neurodegenerative problems”
Fatemeh Kalantarifard, Postdoctoral Researcher, Technical College of Denmark
Supply:
Researchers use tiny diamonds to create intracellular sensors | Information Releases | Optica (2023). Obtainable at: https://www.optica.org/en-us/about/newsroom/news_releases/2023/march/researchers_use_tiny_diamonds_to_create_intracellu/


