
A brand new malware botnet was found concentrating on Realtek SDK, Huawei routers, and Hadoop YARN servers to recruit gadgets into DDoS (distributed denial of service) swarm with the potential for large assaults.
The brand new botnet was found by researchers at Akamai firstly of the 12 months, who caught it on their HTTP and SSH honeypots, seen exploiting outdated flaws comparable to CVE-2014-8361 and CVE-2017-17215.
Akamai feedback that HinataBot’s operators initially distributed Mirai binaries, whereas HinataBot first appeared in mid-January 2023. It appears to be primarily based on Mirai and is a Go-based variant of the infamous pressure.
After capturing a number of samples from energetic campaigns as not too long ago as March 2023, Akamai’s researchers deduced that the malware is beneath energetic growth, that includes useful enhancements and anti-analysis additions.
Vital DDoS energy
The malware is distributed by brute-forcing SSH endpoints or utilizing an infection scripts and RCE payloads for recognized vulnerabilities.
After infecting gadgets, the malware will quietly run, ready for instructions to execute from the command and management server.
Akamai’s analysts created a C2 of their very own and interacted with simulated infections to stage HinataBot for DDoS assaults to look at the malware in motion and infer its assault capabilities.
Older variations of HinataBot supported HTTP, UDP, ICMP, and TCP floods, however the newer variants solely function the primary two. Nevertheless, even with solely two assault modes, the botnet can doubtlessly carry out very highly effective distributed denial of service assaults.
Whereas the HTTP and UDP assault instructions differ, they each create a employee pool of 512 employees (processes) that ship hardcoded information packets to the targets for an outlined period.
The HTTP packet measurement ranges between 484 and 589 bytes. The UDP packets generated by HinataBot are significantly giant (65,549 bytes) and include null bytes able to overwhelming the goal with a big site visitors quantity.
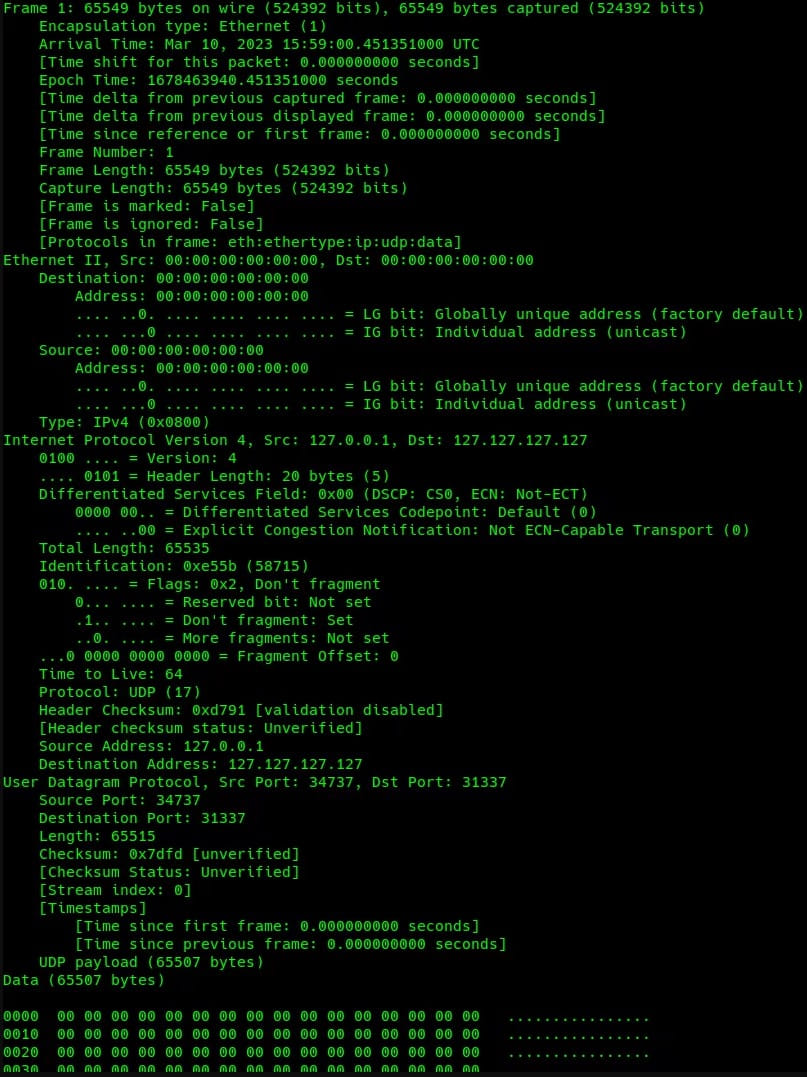
HTTP floods generate giant volumes of web site requests, whereas UDP flood sends giant volumes of rubbish site visitors to the goal; therefore the 2 strategies try to attain an outage utilizing a special strategy.
Akamai benchmarked the botnet in 10-second assaults for each HTTP and UDP, and within the HTTP assault, the malware generated 20,430 requests for a complete measurement of three.4 MB. The UDP flood generated 6,733 packages totaling 421 MB of information.
The researchers estimated that with 1,000 nodes, the UDP flood might generate roughly 336 Gbps, whereas at 10,000 nodes, the assault information quantity would attain 3.3 Tbps.
Within the case of the HTTP flood, 1,000 ensnared gadgets would generate 2,000,000 requests per second, whereas 10,000 nodes would take that variety of 20,400,000 rps and 27 Gbps.
HinataBot continues to be in growth and may implement extra exploits and widen its concentrating on scope anytime. Moreover, the truth that its growth is so energetic will increase the chance of seeing stronger variations circulating within the wild quickly.
“These theorized capabilities clearly do not consider the totally different sorts of servers that will be taking part, their respective bandwidth and {hardware} capabilities, and many others., however you get the image,” warns Akamai.
“Let’s hope that the HinataBot authors transfer onto new hobbies earlier than we’ve to take care of their botnet at any actual scale.”

