Movies have change into an more and more essential a part of our day by day lives, spanning fields resembling leisure, training, and communication. Understanding the content material of movies, nonetheless, is a difficult activity as movies usually comprise a number of occasions occurring at totally different time scales. For instance, a video of a musher hitching up canines to a canine sled earlier than all of them race away includes an extended occasion (the canines pulling the sled) and a brief occasion (the canines being hitched to the sled). One technique to spur analysis in video understanding is through the duty of dense video captioning, which consists of temporally localizing and describing all occasions in a minutes-long video. This differs from single picture captioning and commonplace video captioning, which consists of describing brief movies with a single sentence.
Dense video captioning techniques have vast purposes, resembling making movies accessible to folks with visible or auditory impairments, robotically producing chapters for movies, or enhancing the search of video moments in massive databases. Present dense video captioning approaches, nonetheless, have a number of limitations — for instance, they usually comprise extremely specialised task-specific parts, which make it difficult to combine them into highly effective basis fashions. Moreover, they’re usually educated completely on manually annotated datasets, that are very troublesome to acquire and therefore will not be a scalable answer.
On this submit, we introduce “Vid2Seq: Massive-Scale Pretraining of a Visible Language Mannequin for Dense Video Captioning”, to seem at CVPR 2023. The Vid2Seq structure augments a language mannequin with particular time tokens, permitting it to seamlessly predict occasion boundaries and textual descriptions in the identical output sequence. With a purpose to pre-train this unified mannequin, we leverage unlabeled narrated movies by reformulating sentence boundaries of transcribed speech as pseudo-event boundaries, and utilizing the transcribed speech sentences as pseudo-event captions. The ensuing Vid2Seq mannequin pre-trained on tens of millions of narrated movies improves the cutting-edge on quite a lot of dense video captioning benchmarks together with YouCook2, ViTT and ActivityNet Captions. Vid2Seq additionally generalizes nicely to the few-shot dense video captioning setting, the video paragraph captioning activity, and the usual video captioning activity. Lastly, we’ve additionally launched the code for Vid2Seq right here.
 |
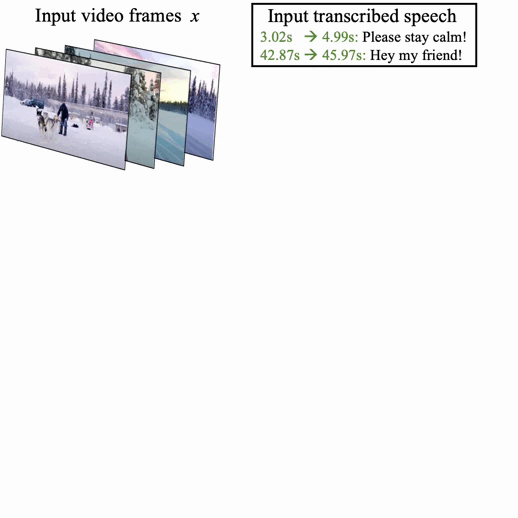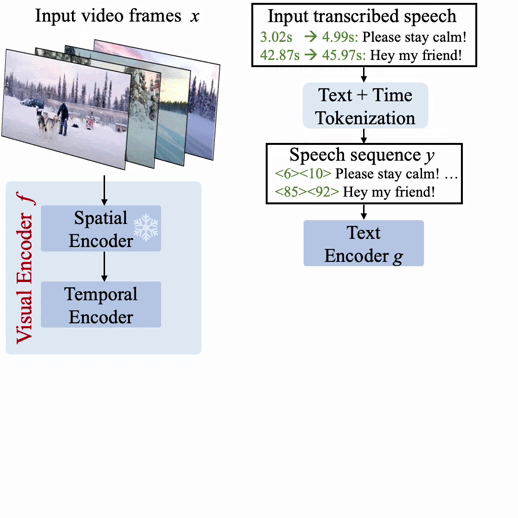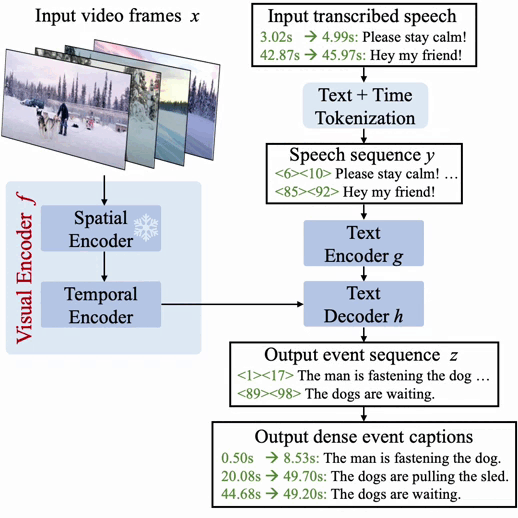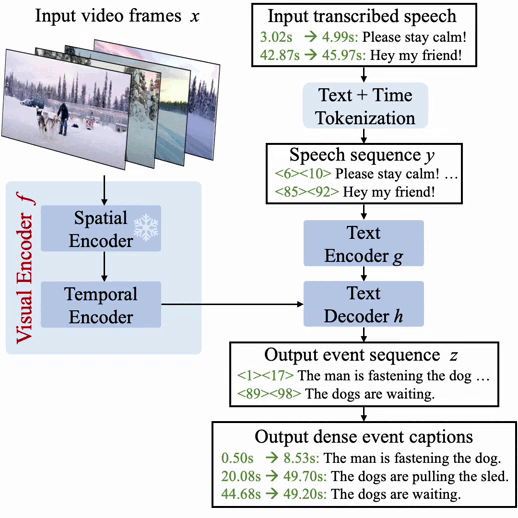
| Vid2Seq is a visible language mannequin that predicts dense occasion captions along with their temporal grounding in a video by producing a single sequence of tokens. |
A visible language mannequin for dense video captioning
Multimodal transformer architectures have improved the cutting-edge on a variety of video duties, resembling motion recognition. Nonetheless it’s not easy to adapt such an structure to the advanced activity of collectively localizing and captioning occasions in minutes-long movies.
For a normal overview of how we obtain this, we increase a visible language mannequin with particular time tokens (like textual content tokens) that signify discretized timestamps within the video, just like Pix2Seq within the spatial area. Given visible inputs, the ensuing Vid2Seq mannequin can each take as enter and generate sequences of textual content and time tokens. First, this allows the Vid2Seq mannequin to grasp the temporal data of the transcribed speech enter, which is forged as a single sequence of tokens. Second, this enables Vid2Seq to collectively predict dense occasion captions and temporally floor them within the video whereas producing a single sequence of tokens.
The Vid2Seq structure features a visible encoder and a textual content encoder, which encode the video frames and the transcribed speech enter, respectively. The ensuing encodings are then forwarded to a textual content decoder, which autoregressively predicts the output sequence of dense occasion captions along with their temporal localization within the video. The structure is initialized with a highly effective visible spine and a robust language mannequin.
Massive-scale pre-training on untrimmed narrated movies
As a result of dense nature of the duty, the handbook assortment of annotations for dense video captioning is especially costly. Therefore we pre-train the Vid2Seq mannequin utilizing unlabeled narrated movies, that are simply accessible at scale. Specifically, we use the YT-Temporal-1B dataset, which incorporates 18 million narrated movies masking a variety of domains.
We use transcribed speech sentences and their corresponding timestamps as supervision, that are forged as a single sequence of tokens. We pre-train Vid2Seq with a generative goal that teaches the decoder to foretell the transcribed speech sequence given visible inputs solely, and a denoising goal that encourages multimodal studying by requiring the mannequin to foretell masked tokens given a loud transcribed speech sequence and visible inputs. Specifically, noise is added to the speech sequence by randomly masking out spans of tokens.
 |
| Vid2Seq is pre-trained on unlabeled narrated movies with a generative goal (prime) and a denoising goal (backside). |
Outcomes on downstream dense video captioning benchmarks
The ensuing pre-trained Vid2Seq mannequin could be fine-tuned on downstream duties with a easy most chance goal utilizing instructor forcing (i.e., predicting the subsequent token given earlier ground-truth tokens). After fine-tuning, Vid2Seq notably improves the cutting-edge on three commonplace downstream dense video captioning benchmarks (ActivityNet Captions, YouCook2 and ViTT) and two video clip captioning benchmarks (MSR-VTT, MSVD). In our paper we offer further ablation research, qualitative outcomes, in addition to leads to the few-shot settings and within the video paragraph captioning activity.
 |
| Comparability to state-of-the-art strategies for dense video captioning (left) and for video clip captioning (proper), on the CIDEr metric (larger is healthier). |
Conclusion
We introduce Vid2Seq, a novel visible language mannequin for dense video captioning that merely predicts all occasion boundaries and captions as a single sequence of tokens. Vid2Seq could be successfully pretrained on unlabeled narrated movies at scale, and achieves state-of-the-art outcomes on varied downstream dense video captioning benchmarks. Study extra from the paper and seize the code right here.
Acknowledgements
This analysis was performed by Antoine Yang, Arsha Nagrani, Paul Hongsuck Web optimization, Antoine Miech, Jordi Pont-Tuset, Ivan Laptev, Josef Sivic and Cordelia Schmid.