As a developer, I naturally need my software program to be dependable and responsive. Within the early days of my profession, suggestions on my purposes was blended. Some apps scored excessive reward, however evaluations had been inconsistent on different apps as a result of they’d intermittently cease responding midsession—and everyone knows how little persistence finish customers have for poor program responsiveness.
The underlying difficulty was that the apps had been coded utilizing purely synchronous JavaScript. Since JavaScript affords (seemingly) asynchronous capabilities, it’s straightforward to overlook the truth that JavaScript’s runtime itself is synchronous by default, and it is a potential pitfall for builders. My curiosity drove me to analyze this programmatic puzzle.
The Downside: JavaScript Synchronous Blocking
I began my exploration by observing the best way that common, synchronous calls work, focusing my efforts on name stacks—final in, first out (LIFO) programming constructions.
All name stacks perform alike, whatever the language: We push (add) perform calls to the stack after which pop (take away) them as wanted.
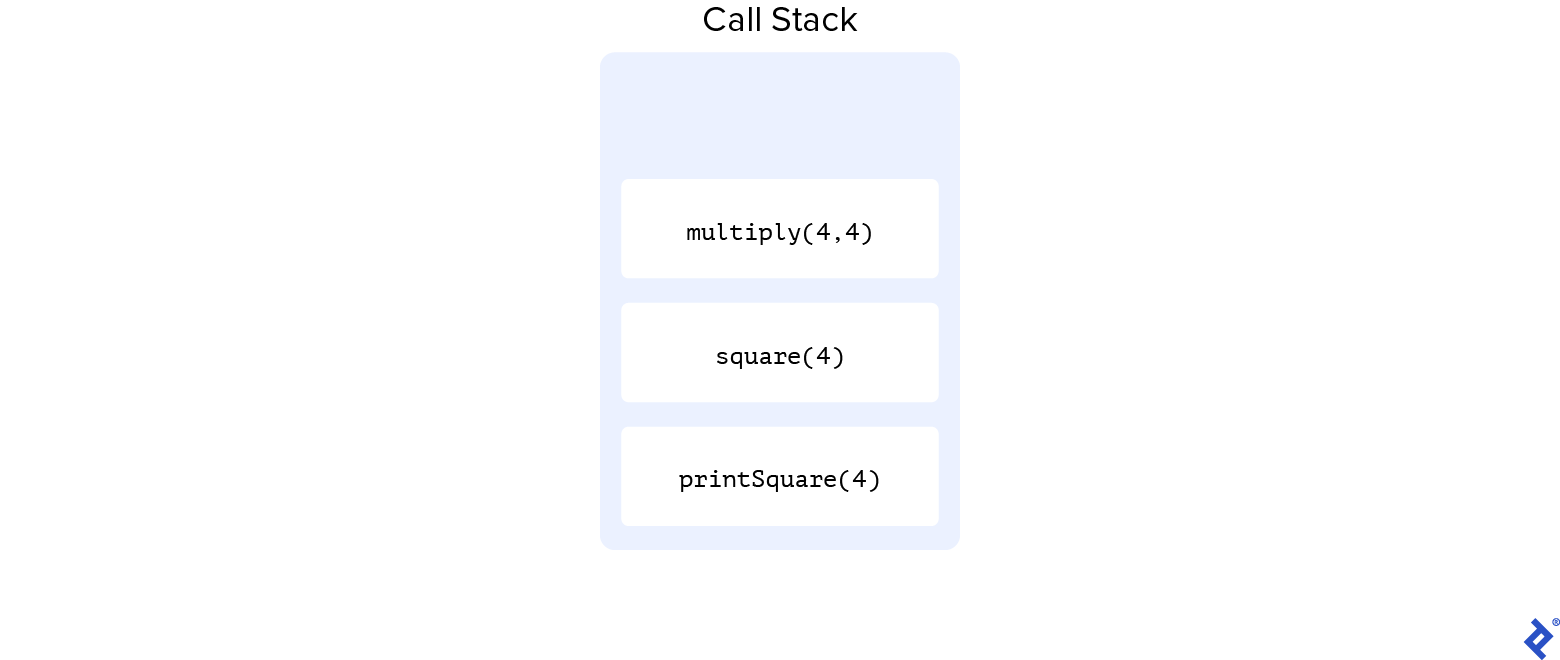
Let’s contemplate a brief instance:
perform multiply(a, b) {
return a * b;
}
perform sq.(n) {
return multiply(n, n);
}
perform printSquare(n) {
const squaredNum = sq.(n);
console.log(squaredNum);
}
printSquare(4);
In our instance, the outermost perform, printSquare, calls the sq. perform, which in flip calls multiply. Features are added to our name stack within the order they’re encountered. As every methodology is accomplished, it’s faraway from the top of the decision stack (i.e., multiply can be eliminated first).
Because the name stack is synchronous, when a number of of those capabilities takes important time to finish, the remaining duties are blocked. Our program turns into unresponsive—at the least quickly—and resumes solely when the blocked perform is accomplished.
Frequent perform calls leading to these program delays embrace:
- A
whereasloop with a excessive iteration rely (e.g., from one to 1 trillion). - A community request to an exterior internet server.
- An occasion that waits for a timer to finish.
- Picture processing.
For finish customers in an online browser, synchronous name blockages lead to an incapability to work together with web page parts. And for builders, these caught calls make the event console inaccessible and take away the flexibility to look at detailed debugging info.
The Answer: Asynchronous JavaScript Performance
Asynchronous coding is a programming approach through which, after we invoke a perform, the rest of our code can run with out having to attend for the preliminary perform to return. When an asynchronous job completes, the JavaScript runtime passes the end result to a perform of our selecting. This methodology eliminates obstacles for our finish customers and builders.
JavaScript implements asynchronous performance by way of a number of key architectural elements:
Something that should run asynchronously (e.g., a timer or exterior API name) is distributed to the runtime engine’s browser API (internet API). The browser API spawns a single execution thread per operation routed its method.
Every asynchronous JavaScript perform name despatched to the browser API has a corresponding promise that enables handler code to be triggered when the perform completes (both efficiently or unsuccessfully). When the perform completes—no matter whether or not it returns a price—its return fulfills its related promise, and the perform strikes from the browser API into JavaScript’s job queue.
The important thing participant in JavaScript’s asynchronous processing is its occasion loop. The occasion loop repeatedly checks if the decision stack and job queue are empty, and coordinates when these accomplished asynchronous calls must be pushed again onto the principle name stack.
Let’s now look at JavaScript’s setTimeout methodology to see JavaScript’s asynchronous methodology dealing with in motion:
perform a() {
b();
}
perform b() {
setTimeout(() => {
console.log("After 5 secs");
}, 5000);
}
perform c() {
console.log("Hey World");
}
a();
c();
Let’s stroll by the code:
-
agoes to the decision stack. -
b’ssetTimeoutinvocation is moved to the browser API name stack. -
cgoes to the decision stack. -
c’sconsole.logname pushes onto the decision stack. - When the
setTimeoutmethodology completes, it’s moved from the browser API to the duty queue. - Any capabilities inside the name stack course of to completion.
- When the decision stack empties, the occasion loop strikes the
setTimeout’s perform from the duty queue again into the decision stack.
Software program engineers can increase their growth capabilities by the appliance of those JavaScript asynchronous strategies. Now that we’ve got seen how asynchronous strategies inside the JavaScript runtime are dealt with, I’ll exhibit their applicability with a brief instance.
Actual-world Purposes: A Chatbot Instance
I lately developed a browser-based chatbot. Synchronous conduct would have been undesirable as it could trigger the dialog to seem disjointed and sluggish. My resolution achieves well-paced dialog by asynchronously speaking with the ChatGPT exterior API to each ship and obtain messages.
To facilitate communication with the ChatGPT API, I created a easy Node.js server utilizing OpenAI. Then I leveraged the asynchronous JavaScript fetch API that makes use of programmatic guarantees to supply a option to entry and course of responses:
fetch('http://localhost:5000/', {
methodology: 'POST',
headers: {
'Content material-Sort': 'utility/json'
},
physique: JSON.stringify({
question: 'What's the climate like in Seattle?'
})
})
.then(response => response.json())
.then(knowledge => {
console.log(knowledge);
});
Our easy server asynchronously calls the ChatGPT service whereas offering bidirectional message transmission.
One other asynchronous methodology I generally use is setInterval(). This perform offers a built-in timer that subsequently calls a perform repeatedly at any specified interval. Utilizing setInterval, I added a typing impact to the consumer interface, letting the consumer know that the opposite celebration (the chatbot) is making a response:
// Creating loader perform for bot
perform loader(aspect) {
aspect.textContent = '';
// 300 ms permits for real-time responsiveness indicating other-party typing
loadInterval = setInterval(() => {
aspect.textContent += '.';
if (aspect.textContent === '....') {
aspect.textContent = '';
}
}, 300);
}
// Creating typing performance
perform typeText(aspect, textual content) {
let index = 0;
// 20 ms permits for real-time responsiveness to imitate chat typing
let interval = setInterval(() => {
if (index < textual content.size) {
aspect.innerHTML += textual content.charAt(index);
index++;
} else {
clearInterval(interval);
}
}, 20);
}
These two asynchronous blocks flip an in any other case disjointed dialog into one through which members really feel engaged. However the responsiveness asynchronous JavaScript permits could also be a much less apparent key ingredient in different contexts.
Extra Asynchronous JavaScript Examples
As soon as I used to be tasked with making a customized WordPress plugin that allowed customers to add massive recordsdata asynchronously. I used an AJAX library to permit the consumer to add their recordsdata within the background with out having to attend for the web page to reload. This allowed for a a lot smoother consumer expertise and the appliance was an enormous success.
In one other use case, an e-commerce web site was having bother with sluggish loading instances as a result of massive variety of photos it needed to load. To hurry up the method, I carried out an async JavaScript perform (LazyLoading) to load every picture asynchronously. This allowed the web site to load quicker, as the photographs weren’t all loaded on the identical time.
I additionally labored on a undertaking involving a cash switch utility integrating varied crypto and fee APIs. I wanted to tug knowledge from an exterior API, however the API took a while to reply. To make sure that the appliance didn’t grind to a halt whereas ready for the API, I carried out an async perform that was in a position to hold the appliance operating whereas it waited for the API response, leading to an enhanced consumer expertise.
Asynchronous strategies in a JavaScript implementation enable for highly effective performance within the service of finish customers, decreasing UI slowdowns or freezes. That’s why asynchronous JavaScript is essential to consumer retention in apps like Uber (operating its reserving and fee processes within the background), Twitter (loading the newest tweets in actual time), and Dropbox (preserving customers’ recordsdata synced and updated throughout gadgets).
As a developer, you could fear that asynchronous JavaScript strategies received’t seem on the decision stack as anticipated—however relaxation assured, they do. Chances are you’ll confidently embrace asynchronous performance amongst your choices in delivering superior consumer experiences.
The Toptal Engineering Weblog extends its gratitude to Muhammad Asim Bilal for reviewing the technical content material and code samples introduced on this article.