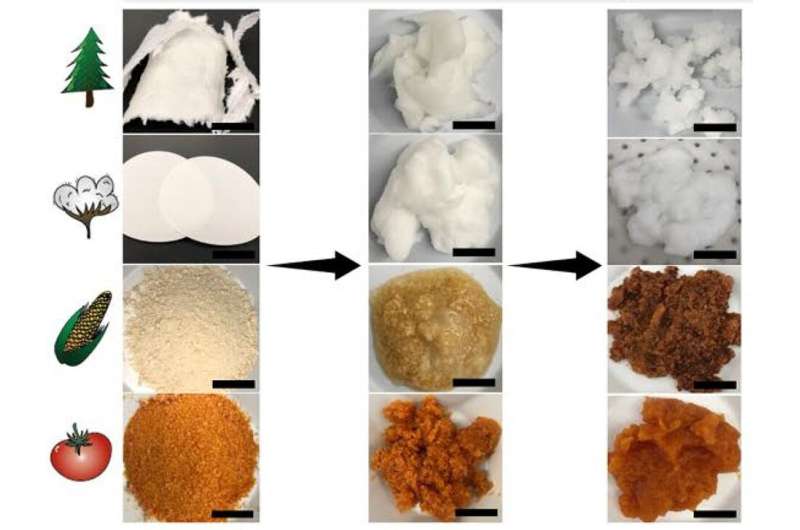
What do corncobs and tomato peels must do with electronics? They each can be utilized to salvage invaluable uncommon earth components, like neodymium, from digital waste. Penn State researchers used micro- and nanoparticles created from the natural supplies to seize uncommon earth components from aqueous options.
Their findings, accessible on-line now, will even be revealed within the November subject of the Chemical Engineering Journal.
“Waste merchandise like corncobs, wooden pulp, cotton and tomato peels typically find yourself in landfills or in compost,” stated corresponding creator Amir Sheikhi, assistant professor of chemical engineering. “We wished to remodel these waste merchandise into micro- or nanoscale particles able to extracting uncommon earth components from digital waste.”
Uncommon earth metals are used to fabricate sturdy magnets utilized in motors for electrical and hybrid vehicles, loudspeakers, headphones, computer systems, wind generators, TV screens and extra. Nonetheless, mining these metals proves difficult and environmentally pricey, in accordance with Sheikhi, as massive land areas are required to mine even small quantities of the metals. As a substitute, efforts have turned to recycling the metals from digital waste objects like outdated computer systems or circuit boards.
The problem lies in effectively separating the metals from refuse, Sheikhi stated.
“Utilizing the natural supplies as a platform, we created extremely purposeful micro- and nanoparticles that may connect to metals like neodymium and separate them from the fluid that surrounds them,” Sheikhi stated. “Through electrostatic interactions, the negatively-charged micro- and nano-scale supplies bind to positively-charged neodymium ions, separating them.”
To arrange the experiment, Sheikhi’s crew floor up tomato peel and corncob and reduce wooden pulp and cotton paper into small, skinny items and soaked them in water. Then, they chemically reacted these supplies in a managed trend to disintegrate them into three distinct fractions of purposeful supplies: microproducts, nanoparticles and solubilized biopolymers. Including the microproducts or nanoparticles to neodymium options triggered the separation course of, ensuing within the seize of neodymium samples.
On this most up-to-date paper, Sheikhi improved upon the separation course of demonstrated in earlier work and extracted bigger pattern sizes of neodymium from much less concentrated options.
Sheikhi plans to increase his separation mechanism into real-world situations and companion with industries to additional take a look at the method.
“Within the close to future, we wish to take a look at our course of on practical industrial samples,” Sheikhi stated.
“We additionally hope to tune the selectivity of the supplies towards different uncommon earth components and valuable metals, like gold and silver, to have the ability to separate these from waste merchandise as nicely.”
Mica L. Pitcher et al, Extremely purposeful bio-based micro- and nano-structured supplies for neodymium restoration, Chemical Engineering Journal (2022). DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2022.137418
Quotation:
Compost to pc: Bio-based supplies used to salvage uncommon earth components (2022, August 19)
retrieved 19 August 2022
from https://phys.org/information/2022-08-compost-bio-based-materials-salvage-rare.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for data functions solely.


