Google mentioned Tuesday it’s making a number of modifications to the Chrome browser to make it much less of a MacBook battery hog. Modifications embrace adjusting timers to wake the CPU much less typically, tuning reminiscence compression and additional optimizing Vitality Saver mode.
The corporate’s checks utilizing a 13-inch M2 MacBook Professional recommend the tweaks could assist of us browse for 17 hours or watch YouTube for 18 hours on a single cost.
Google goes beneath Chrome’s hood to assist enhance MacBook battery life
The modifications comply with latest tweaks to Chrome’s Reminiscence Saver and Vitality Saver modes. Safari is taken into account lighter and friendlier to numerous sources on a Mac, however Google retains refining Chrome to make it a troublesome competitor, particularly given its intensive feature-set.
Google despatched Cult of Mac a rundown of the most recent modifications:
We made a bunch of under-the-hood enhancements with Chrome to assist maximize battery life on MacBooks, from tweaking timers in order that the CPU wakes up much less typically to advantageous tuning reminiscence compression. Consequently, we discovered that Chrome customers may now roughly browse for 17 hours or watch YouTube for 18 hours on a MacBook Professional (13-inch M2, 2022) on a single cost.
A brand new publish Monday on Google’s The Quick and the Curious weblog additional particulars the most recent enhancements, together with how they need to prolong to older Mac fashions:
“With Chrome’s Vitality Saver mode enabled, you’ll be able to browse half-hour longer on battery,” famous Chrome developer François Doray. “In fact, we care deeply about all our customers, not simply these with the most recent {hardware}. That’s why you’ll additionally see efficiency beneficial properties on older fashions, as nicely.”
Doray outlined the modifications and included some particulars.
Small modifications to iframes
Picture: Google
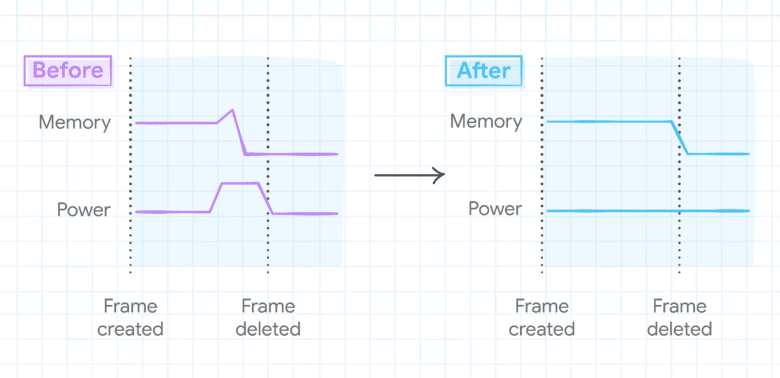
The HTML function referred to as an iframe helps load different parts on a webpage, resembling nesting an HTML web page in an current web page or loading an advert or a video.
“We realized that many iframes dwell only a few seconds,” he mentioned. “Consequently, we fine-tuned the rubbish assortment and reminiscence compression heuristics for just lately created iframes. This leads to much less vitality consumed to cut back short-term reminiscence utilization (with out influence on long-term reminiscence utilization).”
Adjusting Javascript timers
Picture: Google
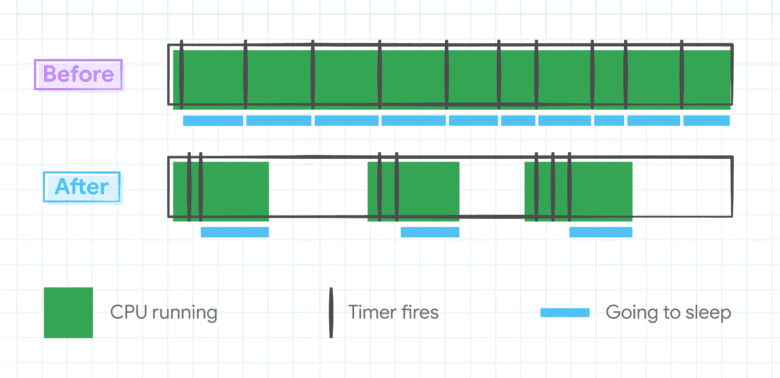
Doray referred to Javascript timers, which have been round because the begin of internet growth. Chrome will better-optimize their use.
“Javascript timers nonetheless drive a big proportion of a Net web page’s energy consumption,” Doray mentioned. “Consequently, we tweaked the best way they hearth in Chrome to let the CPU get up much less typically.”
“Equally, we recognized alternatives to cancel inside timers once they’re now not wanted, lowering the variety of occasions that the CPU is woken up,” he added.
Optimizing entry to knowledge buildings
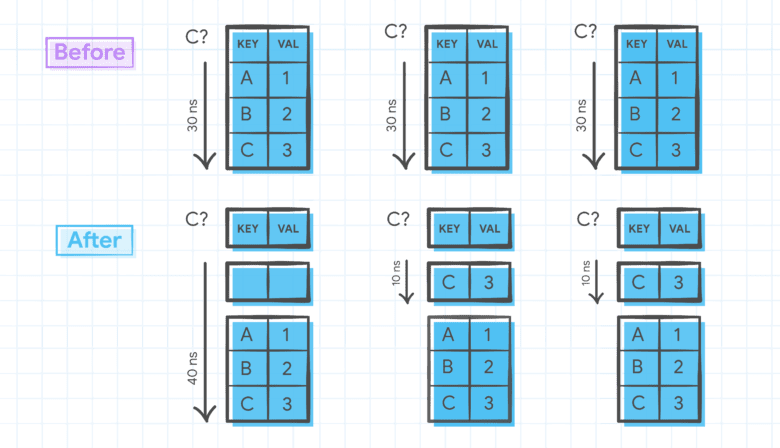
Doray famous that Google recognized often accessed knowledge buildings by the identical key and “optimized their entry sample,” proven under.
Picture: Google
Nixing some web site redraws
Google additionally drew on insights gained by analyzing exterior websites and the way Chrome interacts with them.
“We navigated on real-world websites with a bot and recognized Doc Object Mannequin (DOM) change patterns that don’t have an effect on pixels on the display screen,” Doray mentioned. “We modified Chrome to detect these early and bypass the pointless fashion, format, paint, raster and GPU steps. We carried out related optimizations for modifications to the Chrome UI.”
Lastly, Doray famous this type of work by no means stops, and Google hopes to further-improve Chrome’s battery effectivity with the assistance of a broader neighborhood of builders by means of the open-source benchmark suite.


