
Android malware builders are already adjusting their techniques to bypass a brand new ‘Restricted setting’ safety characteristic launched by Google within the newly launched Android 13.
Android 13 was launched this week, with the brand new working system being rolled out to Google Pixel gadgets and the supply code printed on AOSP.
As a part of this launch, Google tried to cripple cellular malware that tried to allow highly effective Android permissions, similar to AccessibilityService, to carry out malicious, stealthy conduct within the background.
Nonetheless, analysts at Menace Material at this time say malware authors are already creating Android malware droppers that may bypass these restrictions and ship payloads that get pleasure from excessive privileges on a consumer’s gadget.
Android 13 safety
In earlier Android variations, most cellular malware discovered its approach inside hundreds of thousands of gadgets through dropper apps obtainable on the Play Retailer, which masquerade as authentic apps.
Throughout set up, the malware apps immediate customers to grant entry to dangerous permissions after which sideload (or drop) malicious payloads by abusing Accessibility Service privileges.
Accessibility Companies is a massively abused incapacity help system on Android that permits apps to carry out swipes and faucets, return or return to the house display screen. All of that is carried out with out the information or permission of the consumer.
Sometimes, the malware makes use of the service to grant itself further permissions and cease the sufferer from manually deleting the malicious app.
In Android 13, Google’s safety engineers launched a ‘Restricted setting’ characteristic, which blocks sideloaded purposes from requesting Accessibility Service privileges, limiting the operate to Google Play-sourced APKs.
Nonetheless, researchers at ThreatFabric have been in a position to create a proof-of-concept dropper that simply bypassed this new safety characteristic to realize entry to Accessibility Companies.
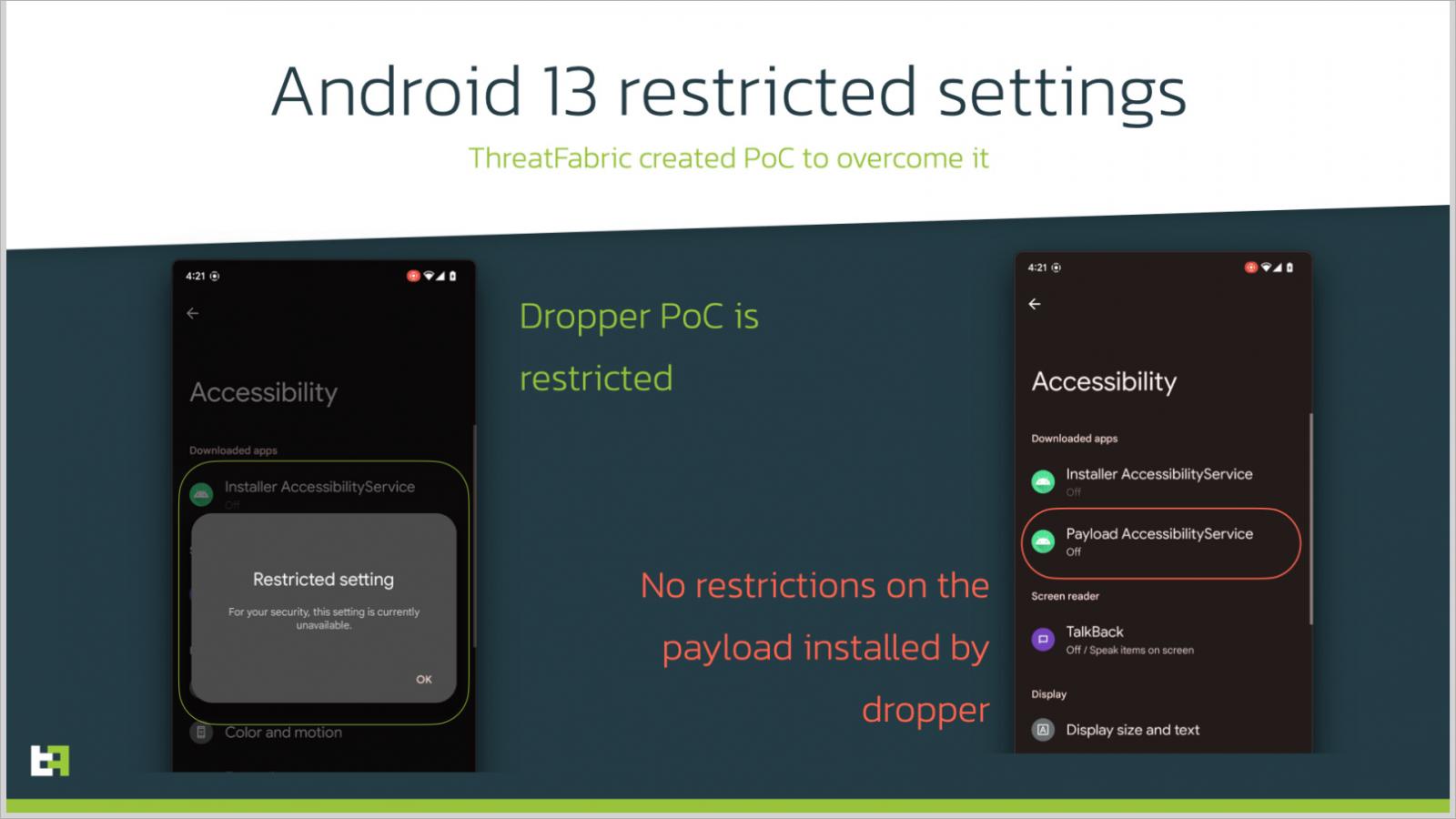
Supply: ThreatFabric
Bypassing Android’s Restricted settings
In a brand new report launched at this time, Menace Material has found a brand new Android malware dropper that’s already including new options to bypass the brand new Restricted setting safety characteristic.
Whereas following the Xenomorph Android malware campaigns, Menace Material found a brand new dropper nonetheless below growth. This dropper was named “BugDrop” after the numerous flaws that plague its operation at this early part.
This novel dropper options code much like Brox, a freely distributed malware growth tutorial venture circulating on hacker boards, however with a modification in a single string of the installer operate.
“What drew our consideration is the presence within the Smali code of the string “com.instance.android.apis.content material.SESSION_API_PACKAGE_INSTALLED,” explains Menace Material within the report.
“This string, which isn’t current within the unique Brox code, corresponds to the motion required by intents to create an set up course of by session.”
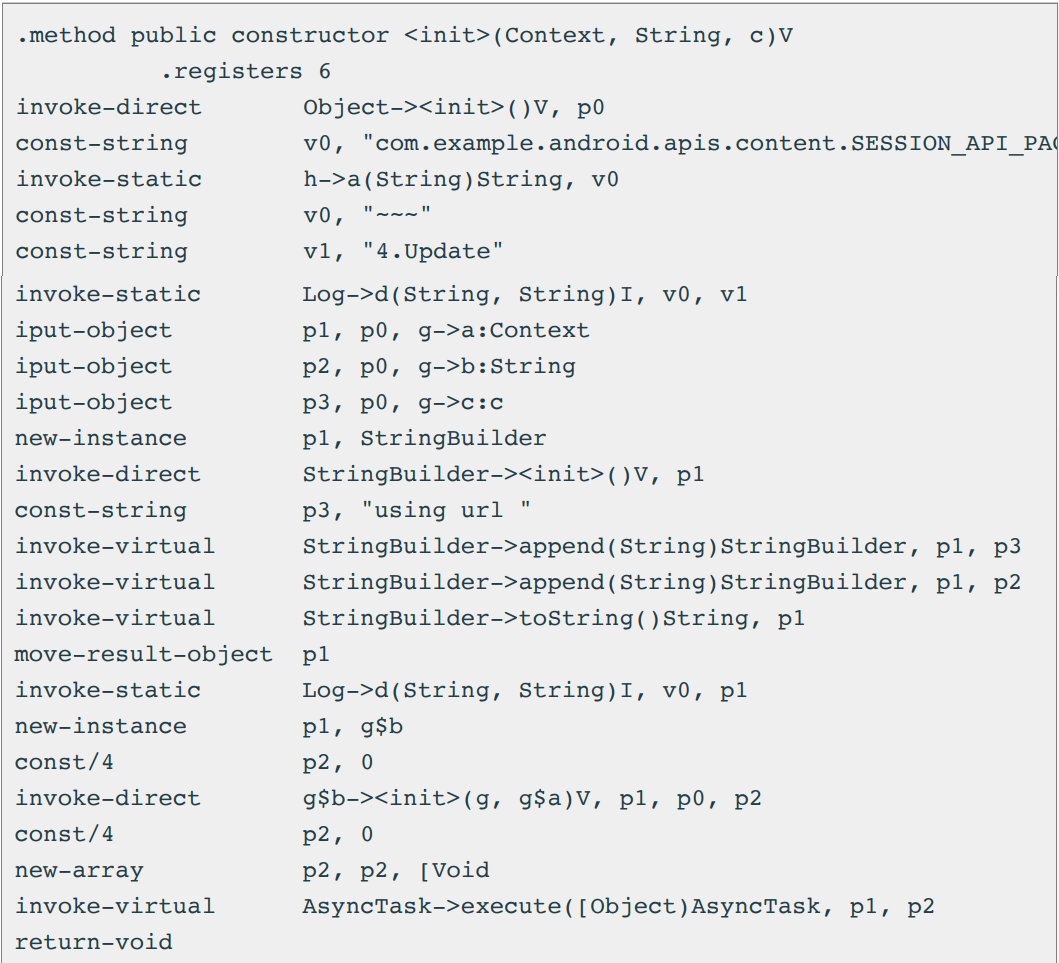
Session-based set up is used to carry out a multi-staged set up of malware onto an Android gadget by splitting the packages (APKs) into smaller items and giving them equivalent names, model codes, and signing certificates.
This manner, Android will not see the payload set up as sideloading the APK, and thus Android 13’s Accessibility Service restrictions will not apply.
“When totally carried out, this slight modification would circumvent Google’s new safety measures totally, even earlier than they’re successfully in place,” feedback Menace Material.
BleepingComputer has reached out to Google with additional questions on this bypass and can replace the story with any response.
Hadoken group
BugDrop continues to be a piece in progress by a bunch of malware authors and operators named ‘Hakoden,’ who’re additionally accountable for creating the Gymdrop dropper and the Xenomorph Android banking trojan.
When BugDrop is prepared for mass deployment, it’s anticipated for use in Xenomorph campaigns, enabling on-device credential theft and fraud conduct on the newest Android gadgets.
Moreover, the most recent Xenomorph samples analyzed by Menace Material have added distant entry trojan (RAT) modules, making the malware an much more potent menace.

