Robots are sometimes outfitted with shifting arms, many instances programmed and used to hold out quite a lot of duties in factories. A lot of these robots have historically had little affiliation with miniature programs that transport small quantities of liquid by way of nice capillaries. These programs, referred to as microfluidics or lab-on-a-chip, normally use exterior pumps to maneuver liquid by way of the chips. Nonetheless, they’ve historically proved troublesome to automate, and the chips have to be custom-designed and manufactured to every particular software.
However now, a group of researchers led by ETH Professor Daniel Ahmed are combining standard robotics and microfluidics. The newly developed gadget makes use of ultrasound and may be connected to a robotic arm. It may additionally perform a variety of duties in micro robotic and micro fluidic functions or used to automate these functions.
The brand new analysis was reported in Nature Communications.
New and Distinctive Machine
The researchers have developed a singular gadget able to creating three-dimensional vortex patterns in liquid by way of using oscillating glass needles powered by piezoelectric transducers – gadgets that are additionally present in loudspeakers, ultrasound imaging and dental cleansing instruments. By adjusting the frequency of those oscillations, they will exactly management their sample formations.
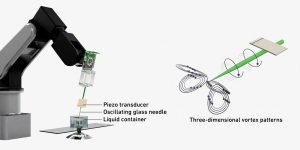
Picture: ETH Zurich
The group used the gadget to show a number of functions, resembling mixing tiny droplets of extremely viscous liquids.
“The extra viscous liquids are, the tougher it’s to combine them,” Ahmed says. “Nonetheless, our methodology suceeds in doing this as a result of it permits us to not solely create a single vortex, however to additionally effectively combine the liquids utilizing a posh three-dimensional sample composed of a number of robust vortices.”
By rigorously manipulating vortices and positioning the oscillating glass needle close to the channel wall, the scientists have been additionally capable of energy their mini-channel system with astonishing effectivity.
By using a robot-assisted acoustic gadget, they have been capable of effectively seize nice particles in fluid. The scale of every particle decided its response to sound waves, inflicting bigger ones to build up round an oscillating glass needle. Remarkably, this similar method was proven succesful not solely of trapping inert particulates but in addition whole fish embryos. With additional growth, the tactic could possibly be used for capturing organic cells from inside fluids as effectively.
“Prior to now, manipulating microscopic particles in three dimensions was at all times difficult. Our microrobotic arm makes it simple,” Ahmed says.
“Till now, developments in massive, standard robotics and microfluidic functions have been made individually,” Ahmed continues. “Our work helps to carry the 2 approaches collectively.

Vortex patterns in liquids Picture: ETH Zurich
As we progress ahead, microfluidic programs of the long run may come near rivaling that of in the present day’s superior robotic expertise. By programming a single gadget with a number of duties resembling mixing and pumping liquids and trapping particles, Ahmed foresees us ushering in an age the place custom-developed chips are not obligatory for every software. Constructing upon this idea additional is the concept to attach numerous glass needles collectively into intricate vortex patterns – pushing our capabilities past what was possible earlier than.
Ahmed envisions an array of potential makes use of for microrobotic arms past the realm of laboratory analysis- something from object sorting and DNA manipulation to additive manufacturing strategies like 3D printing. With these developments, we are able to revolutionize biotechnology as we all know it.


