The standard of a digicam is usually restricted by its measurement and talent to let in a whole lot of mild. In smaller cameras, lenses will help enhance the picture high quality to an extent, however new approaches are as a substitute trying to enhance cameras by modifying the sensors that convert rays of sunshine into electrical indicators.
Three applied sciences offered on the 2023 IEEE Worldwide Electron Machine Assembly (IEDM) promise to enhance the efficiency of CMOS picture sensors by integrating constructions straight into the sensors to steer mild based on its wavelength towards completely different colour pixels. This will increase the quantity of sunshine every pixel receives whereas sustaining a small pixel measurement.
“What you previously achieved solely by complicated system integration is now achieved by wafer-level processes,” says session chair Andreas Mai, professor at Technical College of Utilized Sciences Wildau in Wildau, Germany. In smartphones, for instance, this type of integration might assist cut back the peak of the digicam lens.
At IEDM, researchers from Imec, VisEra, and Samsung reported the invention of three applied sciences to enhance scaled-down picture sensors. Two of those use nano-scale metasurfaces, particularly prisms and pillars, to enhance CMOS sensitivity. The third squeezes mild by way of a colour splitter to type them into completely different colour pixels. “Often, you possibly can solely obtain this by including further parts or lenses on high of the picture sensors,” Mai says.
Shade splitters tune to the human eye
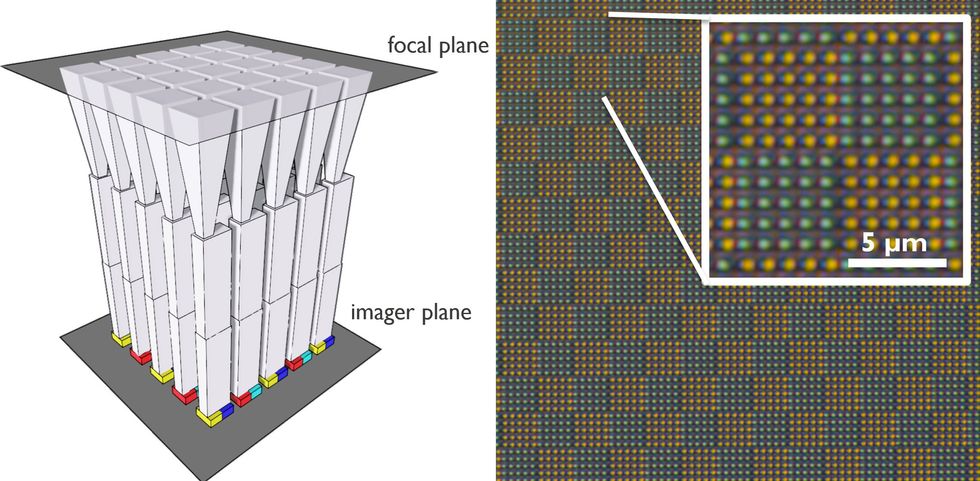
Utilizing colour splitters, a picture sensor can improve its total sensitivity by having mild acceptable to every sensor channeled on to it.
imec
Researchers from Imec—primarily based in Leuven, Belgium—offered colour splitting expertise. As a substitute of utilizing colour filters, which take up a number of the incoming mild, the colour splitter types mild of various colours to particular pixels. Usually, colour splitters work by way of diffraction, however the Imec design takes a unique method, permitting for a greater signal-to-noise ratio and determination.
The colour splitter first takes in mild on the focal aircraft and focuses the sunshine by passing it by way of funnel-shaped tapers, explains Imec’s scientific director Jan Genoe, who offered the analysis at IEDM. The sunshine then passes by way of a vertical waveguide, which restricts the way in which the sunshine propagates and creates wavelength-dependent patterns; so completely different wavelengths of sunshine land on completely different pixels on the detector.
The gadget is designed to be used in small imagers, akin to smartphone cameras, and tuned by way of the waveguide’s dimensions to match the colour sensitivity of the human eye. “We need to have a digicam that provides the very best colour presentation for human eyes,” Genoe says. The gadget offered reveals a 95 % match—even higher than many high-end cameras.
Nano-light pillars carry low-light pictures into focus
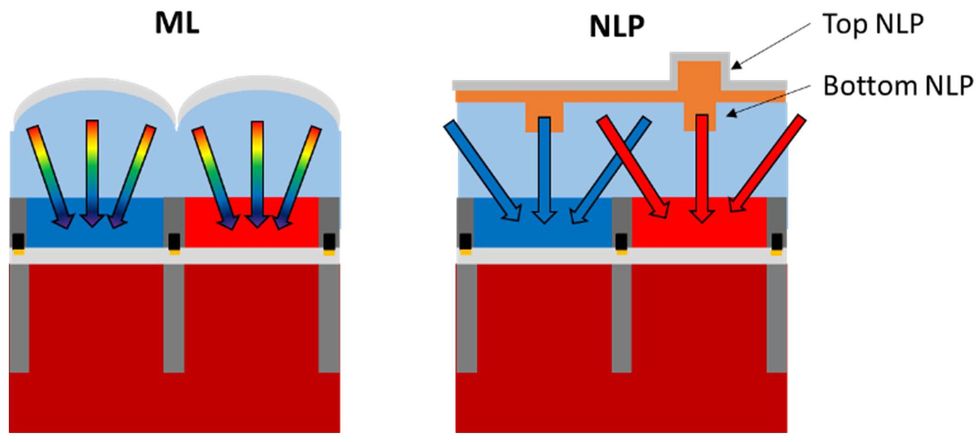
“Nano-pillars” are a lightweight channeling type of a metasurface that, a little bit like Imec’s colour splitter, additionally direct particular wavelengths of sunshine to the detector pixels finest suited to obtain the sunshine.
VisEra Applied sciences
For an additional method to directing mild to particular colour pixels, VisEra Applied sciences—a subsidiary of the Hsinchu, Taiwan-based TSMC—offered a sensor with constructions known as nano-light pillars. Like imec’s colour splitter, the constructions, known as a metasurface, reroute mild of various wavelengths to successfully growing the realm that receives every colour of sunshine. That is notably helpful in low-light circumstances, says Chun-Yuan (Robert) Wang, part supervisor of optics and metrology improvement at VisEra Tech.
The researchers suggest the nano-light pillars as a alternative for standard micro-lenses. With micro-lenses, the light-receiving space is restricted to the bodily dimension of the pixels, and a few mild is at all times misplaced within the pixel’s colour filter. Two layers of fastidiously organized pillars constructed into VisEra’s gadget can collect mild from neighboring pixels by way of refraction: Inexperienced mild heading for a inexperienced pixel for instance, passes straight by way of the pillar. In the meantime, neighboring pillars are designed with completely different densities so that they refract inexperienced mild, sending it to the inexperienced pixel.
Though there are different strategies to enhance imaging in low-light circumstances, these have drawbacks, says Wang. With the metasurface gadget, “you wouldn’t have to resort to utilizing excessive [sensitivity] settings, which introduce noise, or sluggish shutter speeds, which trigger picture blur, to compensate for the dearth of sunshine,” Wang says. The place the VisEra gadget does fall quick is in its response to mild that is available in at an angle due to discontinuities within the metasurface. Wang says he and his colleagues are actually researching options.
Nano-prisms view effectively at an angle
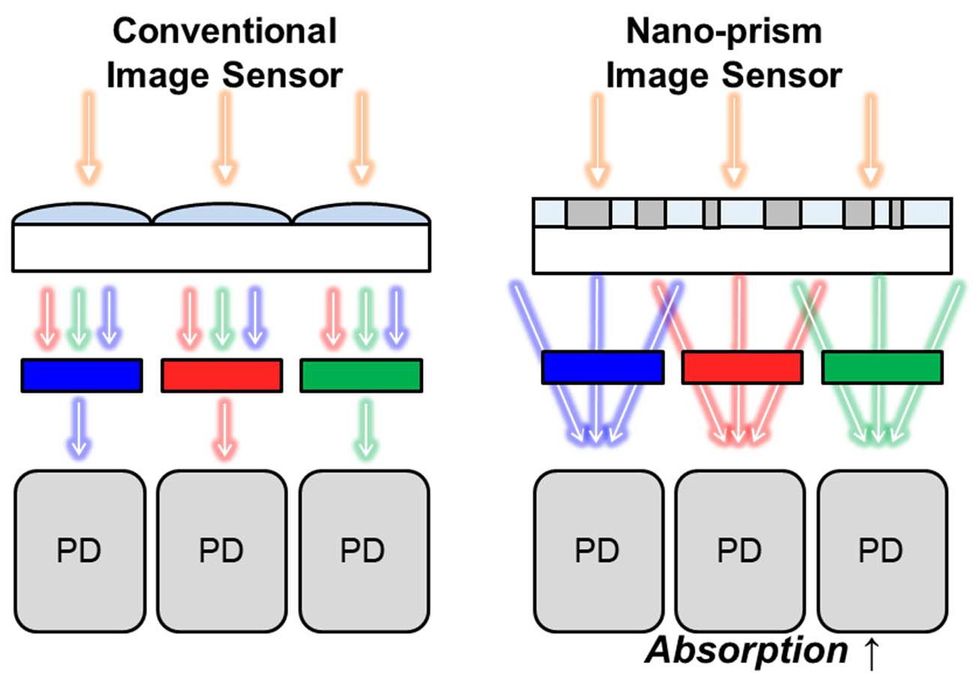
Samsung’s new nano-prism picture has a sensitivity to mild sources at extra indirect angles in comparison with some standard pixel tech at present.
Samsung
Just like the nano-light pillar constructions, nano-prisms—one other metasurface construction—additionally route completely different colours of sunshine to completely different pixels. Samsung’s nano-prisms use diffraction, relatively than refraction, to bend the angle of incoming mild. Moreover, whereas sensitivity to mild at indirect angles is a limitation of VisEra’s pillars, Samsung’s nano-prisms are particularly designed with such a mild in thoughts. In comparison with standard microlenses, they provide a large discipline of view and higher sensitivity.
By altering the sample of the nano-prism design, the researchers may also tweak the spectral response, a measure of the present output by the detector in comparison with the incident energy. Often, this is determined by the fabric of the colour filter, however nano-prisms can regulate the spectral response with out having to alter the colour filter supplies.


